Conserved region 3 of human papillomavirus 16 E7 contributes to deregulation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor
- PMID: 23015707
- PMCID: PMC3503127
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01637-12
Conserved region 3 of human papillomavirus 16 E7 contributes to deregulation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor
Abstract
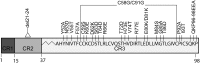
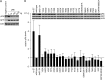
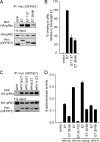
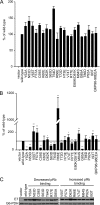
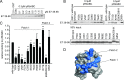
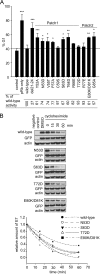
The human papillomavirus (HPV) E7 oncoprotein binds cellular factors, preventing or retargeting their function and thereby making the infected cell conducive for viral replication. A key target of E7 is the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility locus (pRb). This interaction results in the release of E2F transcription factors and drives the host cell into the S phase of the cell cycle. E7 binds pRb via a high-affinity binding site in conserved region 2 (CR2) and also targets a portion of cellular pRb for degradation via the proteasome. Evidence suggests that a secondary binding site exists in CR3, and that this interaction influences pRb deregulation. Additionally, evidence suggests that CR3 also participates in the degradation of pRb. We have systematically analyzed the molecular mechanisms by which CR3 contributes to deregulation of the pRb pathway by utilizing a comprehensive series of mutations in residues predicted to be exposed on the surface of HPV16 E7 CR3. Despite differences in the ability to interact with cullin 2, all CR3 mutants degrade pRb comparably to wild-type E7. We identified two specific patches of residues on the surface of CR3 that contribute to pRb binding independently of the high-affinity CR2 binding site. Mutants within CR3 that affect pRb binding are less effective than the wild-type E7 in overcoming pRb-induced cell cycle arrest. This demonstrates that the interaction between HPV16 E7 CR3 and pRb is functionally important for alteration of the cell cycle.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel retinoblastoma gene product binding site on human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein.J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6842-50. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8120046
-
Structure of the human Papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein and its mechanism for inactivation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 6;281(1):578-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508455200. Epub 2005 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16249186
-
The high-risk HPV16 E7 oncoprotein mediates interaction between the transcriptional coactivator CBP and the retinoblastoma protein pRb.J Mol Biol. 2014 Dec 12;426(24):4030-4048. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.10.021. Epub 2014 Nov 1. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25451029 Free PMC article.
-
The canine papillomavirus and gamma HPV E7 proteins use an alternative domain to bind and destabilize the retinoblastoma protein.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Sep 2;6(9):e1001089. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001089. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20824099 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagenesis of the pRB pocket reveals that cell cycle arrest functions are separable from binding to viral oncoproteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(10):3715-27. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.10.3715-3727.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10779361 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Not-So-Good, the Bad and the Ugly: HPV E5, E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in the Orchestration of Carcinogenesis.Viruses. 2021 Sep 22;13(10):1892. doi: 10.3390/v13101892. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal and Cutaneous Human Papillomavirus Infections and Cancer Biology.Front Oncol. 2019 May 8;9:355. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00355. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31134154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating the human HECT E3 ligases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Sep;75(17):3121-3141. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2848-2. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29858610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angelman syndrome-associated ubiquitin ligase UBE3A/E6AP mutants interfere with the proteolytic activity of the proteasome.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jan 29;6(1):e1625. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.572. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25633294 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of the gamma human papillomavirus type 197 E6 and E7 associated cellular proteins.Virology. 2017 Jan;500:71-81. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Virology. 2017. PMID: 27771561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams A, Gottschling DE, Kaiser CA, Stearns T. 1997. Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
-
- Avvakumov N, Torchia J, Mymryk JS. 2003. Interaction of the HPV E7 proteins with the pCAF acetyltransferase. Oncogene 22:3833–3841 - PubMed
-
- Banks L, et al. 1987. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 polypeptide in cells derived from human cervical carcinomas. J. Gen. Virol. 68(Pt 5):1351–1359 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

