Bcl-x pre-mRNA splicing regulates brain injury after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia
- PMID: 23015448
- PMCID: PMC3482490
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2617-12.2012
Bcl-x pre-mRNA splicing regulates brain injury after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia
Abstract
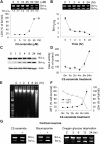
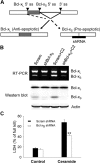
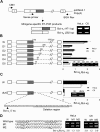
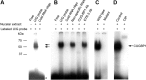
The bcl-x gene appears to play a critical role in regulating apoptosis in the developing and mature CNS and following CNS injury. Two isoforms of Bcl-x are produced as a result of alternative pre-mRNA splicing: Bcl-x(L) (the long form) is anti-apoptotic, while Bcl-x(S) (short form) is pro-apoptotic. Despite the antagonistic activities of these two isoforms, little is known about how regulation of alternative splicing of bcl-x may mediate neural cell apoptosis. Here, we report that apoptotic stimuli (staurosporine or C2-ceramide) reciprocally altered Bcl-x splicing in neural cells, decreasing Bcl-x(L) while increasing Bcl-x(S). Specific knockdown of Bcl-x(S) attenuated apoptosis. To further define regulatory elements that influenced Bcl-x splicing, a Bcl-x minigene was constructed. Deletional analysis revealed several consensus sequences within intron 2 that altered splicing. We found that the splicing factor, CUG-binding-protein-1 (CUGBP1), bound to a consensus sequence close to the Bcl-x(L) 5' splice site, altering the Bcl-x(L)/Bcl-x(S) ratio and influencing cell death. In vivo, neonatal hypoxia-ischemia reciprocally altered Bcl-x pre-mRNA splicing, similar to the in vitro studies. Manipulation of the splice isoforms using viral gene transfer of Bcl-x(S) shRNA into the hippocampus of rats before neonatal hypoxia-ischemia decreased vulnerability to injury. Moreover, alterations in nuclear CUGBP1 preceded Bcl-x splicing changes. These results suggest that alternative pre-mRNA splicing may be an important regulatory mechanism for cell death after acute neurological injury and may potentially provide novel targets for intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C-dependent control of Bcl-x alternative splicing.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;27(24):8431-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00565-07. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17923691 Free PMC article.
-
Relative strength of 5' splice-site strength defines functions of SRSF2 and SRSF6 in alternative splicing of Bcl-x pre-mRNA.BMB Rep. 2021 Mar;54(3):176-181. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.3.170. BMB Rep. 2021. PMID: 33050987 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of alternative splicing of Bcl-x pre-mRNA in prostate and breast cancer cells. analysis of apoptosis and cell death.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 11;276(19):16411-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009256200. Epub 2001 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278482
-
Aberrant Bcl-x splicing in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 12;40(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02001-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34118966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing and programmed cell death.Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1999 Feb;220(2):64-72. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1373.1999.d01-11.x. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1999. PMID: 9933500 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress battles neuronal Bcl-xL in a fight to the death.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Jan;16(1):12-15. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.286946. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32788441 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro analysis of splice site mutations in the CLCN1 gene using the minigene assay.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 May;41(5):2865-74. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3142-5. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24452722
-
Group VIA Phospholipase A2 (iPLA2β) Modulates Bcl-x 5'-Splice Site Selection and Suppresses Anti-apoptotic Bcl-x(L) in β-Cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 24;290(17):11021-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.648956. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25762722 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced alternative splicing: the 11th Hallmark of Cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 15;39(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01616-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32536347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NG25, an inhibitor of transforming growth factor‑β‑activated kinase 1, ameliorates neuronal apoptosis in neonatal hypoxic‑ischemic rats.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jan;17(1):1710-1716. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8024. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Mol Med Rep. 2018. Retraction in: Mol Med Rep. 2025 Mar;31(3):58. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13423 PMID: 29138854 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Al-Zoubi AM, Efimova EV, Kaithamana S, Martinez O, El-Idrissi Mel-A, Dogan RE, Prabhakar BS. Contrasting effects of IG20 and its splice isoforms, MADD and DENN-SV, on tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis and activation of caspase-8 and -3. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:47202–47211. - PubMed
-
- Bae J, Leo CP, Hsu SY, Hsueh AJ. MCL-1S, a splicing variant of the antiapoptotic BCL-2 family member MCL-1, encodes a proapoptotic protein possessing only the BH3 domain. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25255–25261. - PubMed
-
- Barreau C, Paillard L, Méreau A, Osborne HB. Mammalian CELF/Bruno-like RNA-binding proteins: molecular characteristics and biological functions. Biochimie. 2006;88:515–525. - PubMed
-
- Bingle CD, Craig RW, Swales BM, Singleton V, Zhou P, Whyte MK. Exon skipping in Mcl-1 results in a bcl-2 homology domain 3 only gene product that promotes cell death. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22136–22146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
