Modulation of function of sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 1 (SVCT1) by Rab8a in intestinal epithelial cells: studies utilizing Caco-2 cells and Rab8a knockout mice
- PMID: 23014846
- PMCID: PMC3547156
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-012-2388-9
Modulation of function of sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 1 (SVCT1) by Rab8a in intestinal epithelial cells: studies utilizing Caco-2 cells and Rab8a knockout mice
Abstract
Background: Ascorbic acid (AA) is required for normal human health and development. Human intestine expresses two sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters (hSVCT-1 and -2) that mediate cellular AA transport, with hSVCT1 targeting to the apical membrane of polarized epithelia. Studies have shown a role for the Rab8a in the apical membrane targeting of transporters in intestinal cells.
Aims: The purpose of this study was to determine whether Rab8a impacts the function and/or targeting of hSVCT1, and intestinal AA uptake.
Methods: We used human intestinal cells and cells from a Rab8a knockout mouse. (14)C-AA uptake was performed to determine functionality. PCR and western blotting were performed to determine RNA and protein expression, respectively. Confocal imaging was performed to determine co-localization.
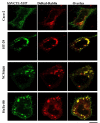
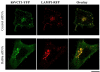
Results: We show that hSVCT1 co-localized with Rab8a in intestinal cells. Knockdown of Rab8a lead to a significant inhibition in AA uptake and cell surface biotinylation studies revealed a lower cell surface expression of hSVCT1 in Rab8a siRNA-treated cells. Similarly, in the small intestine of a Rab8a knockout mouse, AA uptake was significantly inhibited. This effect again resulted from a decreased expression level of mSVCT1 protein, even though mRNA expression of SVCT1 was similar in intestinal cells from Rab8a knockout and wild-type litter-mates. The latter data are suggestive of enhanced lysosomal degradation of hSVCT1 protein in Rab8a-deficient cells; indeed, confocal imaging of Rab8a siRNA-treated intestinal cells revealed a strong overlap between hSVCT1-YFP and LAMP1-RFP.
Conclusions: These findings show a role for Rab8a in the physiological function of hSVCT1 in intestinal epithelia.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors regulate vitamin C transporter functional expression in intestinal epithelial cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2021 Dec;98:108838. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108838. Epub 2021 Aug 14. J Nutr Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34403723
-
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection Inhibits Intestinal Ascorbic Acid Uptake via Dysregulation of Its Transporter Expression.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Jul;66(7):2250-2260. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06389-x. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 32556816 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-103a regulates sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter-1 expression in intestinal epithelial cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Mar;65:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30616065 Free PMC article.
-
The sodium-dependent ascorbic acid transporter family SLC23.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Apr-Jun;34(2-3):436-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.002. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23506882 Review.
-
Functional and physiological role of vitamin C transporters.Curr Top Membr. 2012;70:357-75. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394316-3.00011-9. Curr Top Membr. 2012. PMID: 23177992 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling the cell biology of monogenetic intestinal epithelial disorders.J Cell Biol. 2024 Jul 1;223(7):e202310118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202310118. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38683247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha reduces intestinal vitamin C uptake: a role for NF-κB-mediated signaling.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Aug 1;315(2):G241-G248. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00071.2018. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29631379 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism(s) involved in differential expression of vitamin C transporters along the intestinal tract.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):G340-G347. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00369.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27932501 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of vitamin C homeostasis during deficiency.Nutrients. 2013 Jul 25;5(8):2860-79. doi: 10.3390/nu5082860. Nutrients. 2013. PMID: 23892714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulatory effect on the transport mediated by organic anion transporting polypeptide 2B1.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020 Mar;15(2):181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32373198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Packer L, Fuchs J. Vitamin C in health and disease. Marcel Dekker Inc. 1997
-
- Carr AC, Frei B. Toward a new recommended dietary allowance for vitamin C based on antioxidant and health effects in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69:1086–1107. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Schellhorn HE. New developments and novel therapeutic perspectives for vitamin C. J Nutr. 2007;137:2171–2184. - PubMed
-
- Simon JA, Hudes ES. Serum ascorbic acid and gallbladder disease prevalence among US adults: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:931–936. - PubMed
-
- Boyer JC, Campbell CE, Sigurdson WJ, Kuo SM. Polarized localization of vitamin C transporters, SVCT1 and SVCT2, in epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;334:150–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

