A Phase I clinical trial of the combination of imatinib and paclitaxel in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors refractory to standard therapy
- PMID: 23014737
- PMCID: PMC3703247
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-012-1969-9
A Phase I clinical trial of the combination of imatinib and paclitaxel in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors refractory to standard therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Pre-clinical data suggest that combining imatinib with traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy may improve imatinib efficacy. We conducted a Phase I study of imatinib in combination with paclitaxel in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors.
Methods: Patients were accrued to the study in a standard 3 + 3 design. Patients were restaged every two cycles, and those with stable disease (SD), or better, continued study treatment without interruption. Maximally tolerated doses (MTDs) and pharmacokinetic profiles of combination imatinib and paclitaxel were assessed.
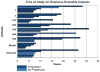
Results: Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, including 40 in the Phase I dose escalation portion. Alternating dose escalation of imatinib and paclitaxel on a 28-day cycle resulted in MTDs of 800 mg imatinib daily, on days 1-4, 8-11, 15-18, and 22-25, and 100 mg/m(2) paclitaxel weekly, on days 3, 10, and 17. Two expansion cohorts, comprising 10 breast cancer patients and 8 patients with soft-tissue sarcomas, were enrolled at the MTDs. The most common adverse events were flu-like symptoms (64 %) and nausea/vomiting (71 %). The most common Grade 3/4 toxicities were neutropenia (26 %), flu-like symptoms (12 %), and pain (12 %). There were no relevant differences in the pharmacokinetic profiles of either drug when given in combination compared with alone. Thirty-eight subjects were evaluable for response, 18 (47.4 %) of whom experienced clinical benefit. Five patients (13.2 %) had a partial response (PR) and 13 patients (34.2 %) had SD; the average time to progression in those with clinical benefit was 17 weeks (range: 7-28 weeks).
Conclusions: This combination of imatinib and paclitaxel was reasonably safe and tolerable, and demonstrated evidence of anti-tumor activity. Further exploration in disease-specific Phase II trials is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A phase I dose-escalation study of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec/STI571) plus capecitabine (Xeloda) in advanced solid tumors.Anticancer Res. 2010 Apr;30(4):1251-6. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20530436 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase 1 trial of imatinib, bevacizumab, and metronomic cyclophosphamide in advanced colorectal cancer.Br J Cancer. 2013 Oct 1;109(7):1725-34. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.553. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24022191 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase II study of pulse dose imatinib mesylate and weekly paclitaxel in patients aged 70 and over with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2012 Oct 3;12:449. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-449. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23033932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
SU2C phase Ib study of paclitaxel and MK-2206 in advanced solid tumors and metastatic breast cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Feb 16;107(3):dju493. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju493. Print 2015 Mar. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015. PMID: 25688104 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I dose escalation trial of weekly docetaxel plus irinotecan in patients with advanced cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2002 Nov-Dec;1(6):646-51. doi: 10.4161/cbt.314. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12642688 Review.
Cited by
-
Multicompartimental nanoparticles for co-encapsulation and multimodal drug delivery to tumor cells and neovasculature.Pharm Res. 2014 May;31(5):1106-19. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1234-x. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24170281
-
The design and discovery of water soluble 4-substituted-2,6-dimethylfuro[2,3-d]pyrimidines as multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and microtubule targeting antitumor agents.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Jul 15;22(14):3753-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.04.049. Epub 2014 May 14. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24890652 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic and Cell Cycle Effects of Triterpenes Isolated from Phoradendron wattii on Leukemia Cell Lines.Molecules. 2022 Aug 31;27(17):5616. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175616. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080390 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal CCL2 Signaling Promotes Mammary Tumor Fibrosis through Recruitment of Myeloid-Lineage Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 28;12(8):2083. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082083. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32731354 Free PMC article.
-
Geminin overexpression promotes imatinib sensitive breast cancer: a novel treatment approach for aggressive breast cancers, including a subset of triple negative.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 30;9(4):e95663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095663. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24789045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S, Segal GM, Fanning S, Zimmermann J, Lydon NB. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med. 1996;2:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian HM, Giles F, Quintas-Cardama A, Cortes J. Important therapeutic targets in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1089–1097. - PubMed
-
- Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Mett H, Meyer T, Muller M, Druker BJ, Lydon NB. Inhibition of the Abl protein-tyrosine kinase in vitro and in vivo by a 2-phenylaminopyrimi-dine derivative. Cancer Res. 1996;56:100–104. - PubMed
-
- Savage DG, Antman KH. Imatinib mesylate—a new oral targeted therapy. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:683–693. - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A, Guilhot F, Schiffer C, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Niederwieser D, Resta D, Capdeville R, Zoellner U, Talpaz M, Druker B, Goldman J, O’Brien SG, Russell N, Fischer T, Ottmann O, Cony-Makhoul P, Facon T, Stone R, Miller C, Tallman M, Brown R, Schuster M, Loughran T, Gratwohl A, Mandelli F, Saglio G, Lazzarino M, Russo D, Baccarani M, Morra E. Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:645–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials