Downregulation of protein kinase CK2 induces autophagic cell death through modulation of the mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in human glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 23007634
- PMCID: PMC3583692
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1635
Downregulation of protein kinase CK2 induces autophagic cell death through modulation of the mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in human glioblastoma cells
Abstract
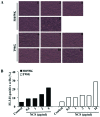
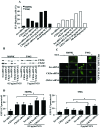
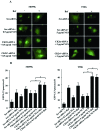
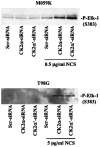
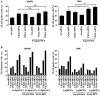
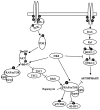
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common primary brain tumor and one of the most aggressive types of cancer in adults. Survival signaling and apoptosis resistance are hallmarks of malignant glioma cells. However, recent studies have shown that other types of cell death such as autophagy can be induced in malignant glioma cells. This suggests that stimulation of this process may be explored in new therapeutic strategies against glioblastoma multiforme. Protein kinase CK2 is a highly conserved and constitutively active enzyme that promotes numerous cellular processes such as survival, proliferation and differentiation. CK2 has been found elevated in several malignancies including brain tumors, and to confer resistance against chemotherapeutic agents and apoptotic stimuli. Recently, we have shown that the siRNA-mediated downregulation of CK2 leads to cell death in DNA-PK-proficient human glioblastoma cells. We show, here, that lack of CK2 results in significant induction of autophagic cell death in two human glioblastoma cell lines, M059K and T98G, as indicated by the positive staining of cells with the acidotropic dye acridine orange, and the specific recruitment of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) to autophagosome membranes. Induction of autophagy is accompanied by CK2-dependent decreased phosphorylation of p70 ribosomal S6 and AKT kinases and significantly reduced expression levels of Raptor. In contrast, phosphorylation and activity levels of ERK1/2 are enhanced suggesting an inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 and activation of the ERK1/2 pathways. Furthermore, siRNA-mediated silencing of CK2 results in increased mitochondrial superoxide production in both glioblastoma cell lines. However, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species release correlates with induction of autophagy only in T98G cells. Taken together, our findings identify CK2 as a novel component of the autophagic machinery and underline the potential of its downregulation to kill glioblastoma cells by overcoming the resistance to multiple anticancer agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of PKCε downregulation on autophagy in glioblastoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2018 Feb 13;18(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4095-1. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29439667 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-apoptotic and pro-autophagic effects of the Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS and MG-63 cells through the activation of mitochondria-mediated pathway and inhibition of p38 MAPK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Mar 12;9:1555-84. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74197. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25792811 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cathepsin S induces autophagy and apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell lines through ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and JNK signaling pathways.Toxicol Lett. 2014 Aug 4;228(3):248-59. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.05.015. Epub 2014 May 27. Toxicol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24875536
-
Autophagic and Apoptotic Pathways as Targets for Chemotherapy in Glioblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 27;19(12):3773. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123773. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30486451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathways and regulation of gene expression in hematopoietic cells.Adv Biol Regul. 2023 May;88:100942. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2022.100942. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Adv Biol Regul. 2023. PMID: 36621151 Review.
Cited by
-
CK2 and the Hallmarks of Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 16;10(8):1987. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081987. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of quercetin on muscle growth and antioxidant status of the dark sleeper Odontobutis potamophila.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 25;13:938526. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.938526. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35957695 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CK2β subunit down-regulation on Akt signalling in HK-2 renal cells.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 7;15(1):e0227340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227340. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31910234 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 inhibition with silmitasertib promotes methuosis-like cell death associated to catastrophic massive vacuolization of colorectal cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 25;10(2):73. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1306-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30683840 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 in Cancer: Cellular and Biochemical Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Target.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017 Jan 28;10(1):18. doi: 10.3390/ph10010018. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28134850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verheij M, Bartelink H. Radiation-induced apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2000;301:133–142. - PubMed
-
- Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R. Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2411–2422. - PubMed
-
- Smith GC, Jackson SP. The DNA-dependent protein kinase. Genes Dev. 1999;13:916–934. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang W, Qin Z, Liang Z. The role of autophagy in sensitizing malignant glioma cells to radiation therapy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2009;41:341–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

