A PHD12-Snail2 repressive complex epigenetically mediates neural crest epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 22986495
- PMCID: PMC3444776
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201203098
A PHD12-Snail2 repressive complex epigenetically mediates neural crest epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
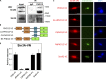
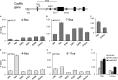
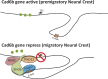
Neural crest cells form within the neural tube and then undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) to initiate migration to distant locations. The transcriptional repressor Snail2 has been implicated in neural crest EMT via an as of yet unknown mechanism. We report that the adaptor protein PHD12 is highly expressed before neural crest EMT. At cranial levels, loss of PHD12 phenocopies Snail2 knockdown, preventing transcriptional shutdown of the adhesion molecule Cad6b (Cadherin6b), thereby inhibiting neural crest emigration. Although not directly binding to each other, PHD12 and Snail2 both directly interact with Sin3A in vivo, which in turn complexes with histone deacetylase (HDAC). Chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed that PHD12 is recruited to the Cad6b promoter during neural crest EMT. Consistent with this, lysines on histone 3 at the Cad6b promoter are hyperacetylated before neural crest emigration, correlating with active transcription, but deacetylated during EMT, reflecting the repressive state. Knockdown of either PHD12 or Snail2 prevents Cad6b promoter deacetylation. Collectively, the results show that PHD12 interacts directly with Sin3A/HDAC, which in turn interacts with Snail2, forming a complex at the Cad6b promoter and thus revealing the nature of the in vivo Snail repressive complex that regulates neural crest EMT.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cadherin-6B proteolysis promotes the neural crest cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through transcriptional regulation.J Cell Biol. 2016 Dec 5;215(5):735-747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201604006. Epub 2016 Nov 17. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27856599 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role for Cadherin6B in regulating avian neural crest emigration.Dev Biol. 2007 Dec 15;312(2):533-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.09.056. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17991460 Free PMC article.
-
Tetraspanin18 is a FoxD3-responsive antagonist of cranial neural crest epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition that maintains cadherin-6B protein.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 15;126(Pt 6):1464-76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.120915. Epub 2013 Feb 15. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23418345 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition: new and old insights from the classical neural crest model.Semin Cancer Biol. 2012 Oct;22(5-6):411-6. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012. PMID: 22575214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Beyond transcription: How post-transcriptional mechanisms drive neural crest EMT".Genesis. 2024 Feb;62(1):e23553. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23553. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Genesis. 2024. PMID: 37735882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Time to go: neural crest cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Development. 2022 Aug 1;149(15):dev200712. doi: 10.1242/dev.200712. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Development. 2022. PMID: 35905012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cadherin-6B proteolysis promotes the neural crest cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through transcriptional regulation.J Cell Biol. 2016 Dec 5;215(5):735-747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201604006. Epub 2016 Nov 17. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27856599 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and migration of neural crest cells in the vertebrate embryo.Histochem Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;138(2):179-86. doi: 10.1007/s00418-012-0999-z. Epub 2012 Jul 22. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22820859 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions during Neural Crest and Somite Development.J Clin Med. 2015 Dec 25;5(1):1. doi: 10.3390/jcm5010001. J Clin Med. 2015. PMID: 26712793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genetic Landscape of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome.Pediatr Cardiol. 2018 Aug;39(6):1069-1081. doi: 10.1007/s00246-018-1861-4. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Pediatr Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29569026 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

