Effects of MACPF/CDC proteins on lipid membranes
- PMID: 22983385
- PMCID: PMC11114033
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1153-8
Effects of MACPF/CDC proteins on lipid membranes
Abstract
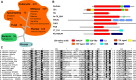
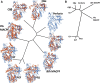
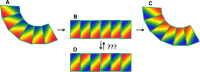
Recent work on the MACPF/CDC superfamily of pore-forming proteins has focused on the structural analysis of monomers and pore-forming oligomeric complexes. We set the family of proteins in context and highlight aspects of their function which the direct and exclusive equation of oligomers with pores fails to explain. Starting with a description of the distribution of MACPF/CDC proteins across the domains of life, we proceed to show how their evolutionary relationships can be understood on the basis of their structural homology and re-evaluate models for pore formation by perforin, in particular. We furthermore highlight data showing the role of incomplete oligomeric rings (arcs) in pore formation and how this can explain small pores generated by oligomers of proteins belonging to the family. We set this in the context of cell biological and biophysical data on the proteins' function and discuss how this helps in the development of an understanding of how they act in processes such as apicomplexan parasites gliding through cells and exiting from cells.
Figures
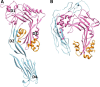
Similar articles
-
Packing a punch: the mechanism of pore formation by cholesterol dependent cytolysins and membrane attack complex/perforin-like proteins.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012 Jun;22(3):342-9. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 May 31. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22658510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;677:56-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6327-7_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20687480 Review.
-
The membrane attack complex, perforin and cholesterol-dependent cytolysin superfamily of pore-forming proteins.J Cell Sci. 2016 Jun 1;129(11):2125-33. doi: 10.1242/jcs.182741. Epub 2016 May 13. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27179071 Review.
-
Structural features of cholesterol dependent cytolysins and comparison to other MACPF-domain containing proteins.Subcell Biochem. 2014;80:47-62. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8881-6_4. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24798007 Review.
-
Distribution of MACPF/CDC proteins.Subcell Biochem. 2014;80:7-30. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8881-6_2. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24798005 Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM structures of perforin-2 in isolation and assembled on a membrane suggest a mechanism for pore formation.EMBO J. 2022 Dec 1;41(23):e111857. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022111857. Epub 2022 Oct 17. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 36245269 Free PMC article.
-
The perforin pore facilitates the delivery of cationic cargos.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):9172-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.544890. Epub 2014 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24558045 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging the lipid-phase-dependent pore formation of equinatoxin II in droplet interface bilayers.Biophys J. 2014 Apr 15;106(8):1630-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.11.4507. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24739162 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of the AGL1 aegerolysin in the mycoparasitic fungus Trichoderma atroviride reveals a role in conidiation and antagonism.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 Jan;296(1):131-140. doi: 10.1007/s00438-020-01732-3. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33052533 Free PMC article.
-
Perforin oligomers form arcs in cellular membranes: a locus for intracellular delivery of granzymes.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Jan;22(1):74-85. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.110. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25146929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosado CJ, Buckle AM, Law RH, Butcher RE, Kan WT, Bird CH, Ung K, Browne KA, Baran K, Bashtannyk-Puhalovich TA, Faux NG, Wong W, Porter CJ, Pike RN, Ellisdon AM, Pearce MC, Bottomley SP, Emsley J, Smith AI, Rossjohn J, Hartland EL, Voskoboinik I, Trapani JA, Bird PI, Dunstone MA, Whisstock JC. A common fold mediates vertebrate defense and bacterial attack. Science. 2007;317:1548–1551. doi: 10.1126/science.1144706. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

