Mechanism of transcription through a nucleosome by RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 22982194
- PMCID: PMC3535581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.015
Mechanism of transcription through a nucleosome by RNA polymerase II
Abstract
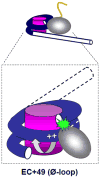
Efficient maintenance of chromatin structure during passage of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is critical for cell survival and functioning. Moderate-level transcription of eukaryotic genes by Pol II is accompanied by nucleosome survival, extensive exchange of histones H2A/H2B and minimal exchange of histones H3/H4. Complementary in vitro studies have shown that transcription through chromatin by single Pol II complexes is uniquely coupled with nucleosome survival via formation of a small intranucleosomal DNA loop (Ø-loop) containing the transcribing enzyme. In contrast, transient displacement and exchange of all core histones are observed during intense transcription. Indeed, multiple transcribing Pol II complexes can efficiently overcome the high nucleosomal barrier and displace the entire histone octamer in vitro. Thus, various Pol II complexes can remodel chromatin to different extents. The mechanisms of nucleosome survival and displacement during transcription and the role of DNA-histone interactions and various factors during this process are discussed. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: RNA polymerase II Transcript Elongation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanism of histone survival during transcription by RNA polymerase II.Transcription. 2010 Sep-Oct;1(2):85-8. doi: 10.4161/trns.1.2.12519. Transcription. 2010. PMID: 21326897 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase complexes cooperate to relieve the nucleosomal barrier and evict histones.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11325-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001148107. Epub 2010 Jun 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534568 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of chromatin remodeling and recovery during passage of RNA polymerase II.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Dec;16(12):1272-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1689. Epub 2009 Nov 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19935686 Free PMC article.
-
Histone dynamics during transcription: exchange of H2A/H2B dimers and H3/H4 tetramers during pol II elongation.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;41:77-90. doi: 10.1007/400_009. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 16909891 Review.
-
Transcription through the nucleosome.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020 Apr;61:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2019.10.007. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 31790919 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleosome adaptability conferred by sequence and structural variations in histone H2A-H2B dimers.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015 Jun;32:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 25731851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of nucleosome transcription mediated by Chd1 and FACT.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Apr;28(4):382-387. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00578-6. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33846633 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of transcribed chromatin is a sensor of DNA damage.Sci Adv. 2015 Jul 3;1(6):e1500021. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500021. eCollection 2015 Jul. Sci Adv. 2015. PMID: 26601207 Free PMC article.
-
Histone turnover and chromatin accessibility: Critical mediators of neurological development, plasticity, and disease.Bioessays. 2016 May;38(5):410-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500171. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 26990528 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin replication: TRANSmitting the histone code.J Nat Sci. 2017 Feb;3(2):e322. J Nat Sci. 2017. PMID: 28393112 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

