Relationships between Lymph Node Metastasis and Expression of CD31, D2-40, and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors A and C in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- PMID: 22977712
- PMCID: PMC3437416
- DOI: 10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.150
Relationships between Lymph Node Metastasis and Expression of CD31, D2-40, and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors A and C in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the relationships between lymph node metastasis (LNM) and expression of CD31, D2-40 and vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF)-A and -C in patients with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC).
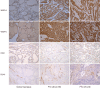
Methods: Paraffin-embedded thyroid tissues of 72 patients were evaluated, which included 25 patients with thyroid nodular hyperplasia (TNH), 24 PTC patients without LNM, and 23 PTC patients with LNM. Three pathologists, who were blinded to the patient's clinical information, assessed the immunohistochemical staining results. The amount of expression was scored as high (>25% of cells stained) or low (0-25%).
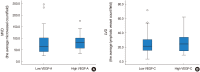
Results: A higher level of VEGF-A expression was observed in the PTC groups regardless of LNM when compared to the group with TNH (91.3%, 79.2%, 4.0%, respectively). VEGF-C expression in the PTC with LNM group was significantly higher than the other two groups (P<0.05). No difference in microvessel density (MVD) scores was observed using CD31 among the three groups. The lymphatic vessel density (LVD) score using D2-40 was significantly higher in patients having PTC with LNM than the other groups (P<0.05).
Conclusion: VEGF-C and D2-40 were more highly expressed in patients having PTC with LNM than in patients having PTC without LNM or in those having TNH. Analysis of VEGF-C level and LVD using D2-40 may be helpful in the diagnosis of PTC and the evaluation of LNM potential in patients with PTC.
Keywords: Lymph node; Metastasis; Papillary carcinoma; Thyroid; VEGF-A; VEGF-C.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interests relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Expression of VEGF-C and angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis in papillary thyroid carcinoma].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006 Jun;31(3):414-6, 419. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006. PMID: 16859137 Chinese.
-
Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C in papillary thyroid carcinoma correlates with cervical lymph node metastases.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Nov 15;11(22):8063-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0646. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16299237
-
Concomitant high expression of survivin and vascular endothelial growth factor-C is strongly associated with metastatic status of lymph nodes in papillary thyroid carcinoma.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(Supplement):S114-S119. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.163675. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29578160
-
Clinical application of the ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for thyroglobulin measurement to diagnose lymph node metastasis from differentiated thyroid carcinoma-literature review.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Apr;36(4):236-243. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12173. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31909556 Review.
-
Correlation between the Expression of VEGF and Ki67 and Lymph Node Metastasis in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 28;2022:9693746. doi: 10.1155/2022/9693746. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9894125. doi: 10.1155/2023/9894125. PMID: 35800006 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of thyroid cancer in Chinese females with breast cancer by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), microvessel density, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS).Tumour Biol. 2014 Jul;35(7):6521-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1868-2. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24687553
-
Relationship between expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and cervical lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Oct;37(5):661-666. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1786-9. Epub 2017 Oct 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29058277
-
Effectiveness of an i-PTH measurement in predicting post thyroidectomy hypocalcemia: prospective controlled study.Yonsei Med J. 2013 May 1;54(3):637-42. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.637. Yonsei Med J. 2013. PMID: 23549808 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between VEGF protein expression and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma among Asians: a meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jun;35(6):5511-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1725-3. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Tumour Biol. 2014. Retraction in: Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(9):7305. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3698-2. PMID: 24557543 Retracted.
-
Arsenic sulfide inhibits cell migration and invasion of gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Oct 9;9:5579-90. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S89805. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26487802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tian X, Cong M, Zhou W, Zhu J, Liu Q. Relationship between protein expression of VEGF-C, MMP-2 and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer. J Int Med Res. 2008 Jul-Aug;36(4):699–703. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi S, Murakami N, Yamashita H, Toda M, Kawamoto H. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: modified radical neck dissection improves prognosis. Arch Surg. 1998 Mar;133(3):276–280. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Houck K, Jakeman L, Leung DW. Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):18–32. - PubMed

