Influence of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-8 receptors on the migration of human keratinocytes, the role of PLC-γ and potential clinical implications
- PMID: 22969874
- PMCID: PMC3438606
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2011.402
Influence of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-8 receptors on the migration of human keratinocytes, the role of PLC-γ and potential clinical implications
Abstract
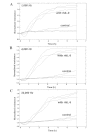
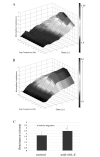
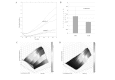
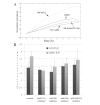
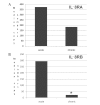
Interleukin (IL)-8 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that has a direct effect on immune cells, including polymorphonuclear cells. Keratinocytes are a rich source of IL-8. However, there is little knowledge on the role of IL-8 in clinical wound healing and the direct biological effect of IL-8 on keratinocytes. In this study, the effect of recombinant human IL-8 (rhIL-8) on migration and adhesion was tested using HaCaT keratinocytes as a cell model. The cell functions were evaluated using impedance cell sensing. The expression of IL-8 receptor (IL-8R) transcripts in human skin and wounds (acute and chronic) was assessed using real-time transcript analysis. rhIL-8 significantly increased the migration of keratinocytes (3.5±0.3 for cells treated with IL-8 vs. 2.7±0.6 for controls; p=0.029). It is interesting to note that treatment of keratinocytes with IL-8 resulted in a marked shift in the responsive frequencies. IL-8 only resulted in a marginal increase in cell adhesion, which was particularly noticeable at high frequencies. The PLC-γ inhibitor completely eradicated the action of IL-8 on the migration of HaCaT cells. Using real time PCR, it was found that chronic wounds had significantly lower levels of the B form of the IL-8R (IL-8RB) (p=0.045) and marginally lower levels of the A form, IL-8RA, in comparison with acute wounds. Therefore, IL-8 has a direct and profound stimulatory effect on the migration of human keratinocytes, which is likely to occur via the PLC-γ pathway. Together with a reduced level of IL-8Rs in difficult-healing wounds, IL-8 has a clear prognostic and therapeutic value in wound healing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The clinical significance and impact of interleukin 15 on keratinocyte cell growth and migration.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Sep;38(3):679-86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2687. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27460304 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of IL-24 and IL-24 receptors in human wound tissues and the biological implications of IL-24 on keratinocytes.Wound Repair Regen. 2012 Nov-Dec;20(6):896-903. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2012.00840.x. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Wound Repair Regen. 2012. PMID: 23110359
-
Potential implications of interleukin-7 in chronic wound healing.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Jul;12(1):33-40. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3263. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27347014 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the expression of IL-8 receptor A/B by IL-8: possible functions of each receptor.J Immunol. 1995 Sep 1;155(5):2587-94. J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7650389
-
Nuclear expression of IL-33 in epidermal keratinocytes promotes wound healing in mice.J Dermatol Sci. 2017 Feb;85(2):106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.10.008. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Dermatol Sci. 2017. PMID: 27839630
Cited by
-
Potential Therapeutic Role of Mesenchymal-Derived Stem Cells as an Alternative Therapy to Combat COVID-19 through Cytokines Storm.Cells. 2022 Aug 29;11(17):2686. doi: 10.3390/cells11172686. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Palmoplantar Pustulosis: Recent Advances in Etiopathogenesis and Emerging Treatments.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020 Jun;21(3):355-370. doi: 10.1007/s40257-020-00503-5. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32008176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital dermatitis in cattle is associated with an excessive innate immune response triggered by the keratinocytes.BMC Vet Res. 2013 Oct 3;9:193. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-193. BMC Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 24090086 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Exosomes From Tick Saliva and Salivary Glands Reveals Therapeutic Roles for CXCL12 and IL-8 in Wound Healing at the Tick-Human Skin Interface.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 16;8:554. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00554. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32766239 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of an Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned medium and TGF-β1 on Human Keratinocytes In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 29;24(19):14726. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914726. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Damme J, Decock B, Conings R, Lenaerts JP, Opdenakker G, Billiau A. The chemotactic activity for granulocytes produced by virally infected fibroblasts is identical to monocyte-derived interleukin 8. Eur J Immunol. 1989;19:1189–1194. - PubMed
-
- Wolpe SD, Cerami A. Macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 and 2: members of a novel superfamily of cytokines. FASEB J. 1989;3:2565–2573. - PubMed
-
- Modi WS, Chen ZQ. Localization of the human CXC chemokine subfamily on the long arm of chromosome 4 using radiation hybrids. Genomics. 1998;47:136–139. - PubMed
-
- Smyth RL, Mobbs K, O’Hea U, Ashby D, Hart CA. The association between disease severity, cytokines and virus genotype in infants with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis. Arch Dis Child. 2000;82(Suppl 1):A4–A5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
