Leucine supplementation increases SIRT1 expression and prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
- PMID: 22967499
- PMCID: PMC3517633
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00198.2012
Leucine supplementation increases SIRT1 expression and prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
Abstract
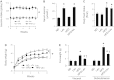
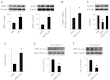
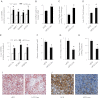
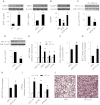
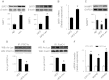
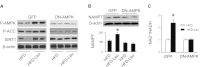
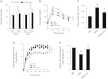
Leucine supplementation has been shown to prevent high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia in animal models, but the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Recent studies suggest that activation of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) is an important mechanism to maintain energy and metabolic homeostasis. We therefore examined the involvement of SIRT1 in leucine supplementation-prevented obesity and insulin resistance. To accomplish this goal, male C57BL/6J mice were fed normal diet or HFD, supplemented with or without leucine. After 2 mo of treatment, alterations in SIRT1 expression, insulin signaling, and energy metabolism were analyzed. Eight weeks of HFD induced obesity, fatty liver, mitochondrial dysfunction, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance in mice. Addition of leucine to HFD correlated with increased expression of SIRT1 and NAMPT (nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase) as well as higher intracellular NAD(+) levels, which decreased acetylation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC1α) and forkhead box O1 (FoxO1). The deacetylation of PGC1α may contribute to upregulation of genes controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and fatty acid oxidation, thereby improving mitochondrial function and preventing HFD-induced obesity in mice. Moreover, decreased acetylation of FoxO1 was accompanied by decreased expression of pseudokinase tribble 3 (TRB3) and reduced the association between TRB3 and Akt, which enhanced insulin sensitivity and improved glucose metabolism. Finally, transfection of dominant negative AMPK prevented activation of SIRT1 signaling in HFD-Leu mice. These data suggest that increased expression of SIRT1 after leucine supplementation may lead to reduced acetylation of PGC1α and FoxO1, which is associated with attenuation of HFD-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance, and obesity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of NAMPT aggravates high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in mice through regulating Sirt1/AMPKα/SREBP1 signaling pathway.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Apr 27;16(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0464-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28449683 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine Activates SIRT1/AMPK/FOXO1 Signaling Pathways to Favorably Regulate Lipid Metabolism in C57BL6 Obese Mice.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024 Apr;68(8):e2200660. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202200660. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024. PMID: 38549461
-
Impairment of energy sensors, SIRT1 and AMPK, in lipid induced inflamed adipocyte is regulated by Fetuin A.Cell Signal. 2018 Jan;42:67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 29030114
-
Leucine Supplementation: A Novel Strategy for Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Energy Homeostasis.Nutrients. 2020 May 2;12(5):1299. doi: 10.3390/nu12051299. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32370170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirt1-PPARS Cross-Talk in Complex Metabolic Diseases and Inherited Disorders of the One Carbon Metabolism.Cells. 2020 Aug 11;9(8):1882. doi: 10.3390/cells9081882. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32796716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gender-Associated Impact of Early Leucine Supplementation on Adult Predisposition to Obesity in Rats.Nutrients. 2018 Jan 12;10(1):76. doi: 10.3390/nu10010076. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29329236 Free PMC article.
-
Polyoxometalates Ameliorate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease by Activating the AMPK Signaling Pathway.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Oct 25;19:10839-10856. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S485084. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39479173 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PGC-1α in the Mitochondrial NAD+ Pool in Metabolic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 27;22(9):4558. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094558. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming and Host Tolerance: A Novel Concept to Understand Sepsis-Associated AKI.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 16;10(18):4184. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184184. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-talk between branched-chain amino acids and hepatic mitochondria is compromised in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Aug 15;309(4):E311-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00161.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26058864 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Anthony JC, Anthony TG, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS. Signaling pathways involved in translational control of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle by leucine. J Nutr 131: 856S– 860S, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, Hu LS, Cheng HL, Jedrychowski MP, Gygi SP, Sinclair DA, Alt FW, Greenberg ME. Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303: 2011– 2015, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

