HYST: a hybrid set-based test for genome-wide association studies, with application to protein-protein interaction-based association analysis
- PMID: 22958900
- PMCID: PMC3511992
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.08.004
HYST: a hybrid set-based test for genome-wide association studies, with application to protein-protein interaction-based association analysis
Abstract
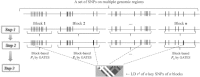
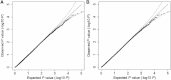
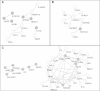
The extended Simes' test (known as GATES) and scaled chi-square test were proposed to combine a set of dependent genome-wide association signals at multiple single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for assessing the overall significance of association at the gene or pathway levels. The two tests use different strategies to combine association p values and can outperform each other when the number of and linkage disequilibrium between SNPs vary. In this paper, we introduce a hybrid set-based test (HYST) combining the two tests for genome-wide association studies (GWASs). We describe how HYST can be used to evaluate statistical significance for association at the protein-protein interaction (PPI) level in order to increase power for detecting disease-susceptibility genes of moderate effect size. Computer simulations demonstrated that HYST had a reasonable type 1 error rate and was generally more powerful than its parents and other alternative tests to detect a PPI pair where both genes are associated with the disease of interest. We applied the method to three complex disease GWAS data sets in the public domain; the method detected a number of highly connected significant PPI pairs involving multiple confirmed disease-susceptibility genes not found in the SNP- and gene-based association analyses. These results indicate that HYST can be effectively used to examine a collection of predefined SNP sets based on prior biological knowledge for revealing additional disease-predisposing genes of modest effects in GWASs.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GATES: a rapid and powerful gene-based association test using extended Simes procedure.Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Mar 11;88(3):283-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.01.019. Am J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21397060 Free PMC article.
-
Gene, pathway and network frameworks to identify epistatic interactions of single nucleotide polymorphisms derived from GWAS data.BMC Syst Biol. 2012;6 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S15. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-S3-S15. Epub 2012 Dec 17. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 23281810 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-SNP association test for complex diseases incorporating an optimal P-value threshold algorithm in nuclear families.BMC Genomics. 2015 May 15;16(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1620-3. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25975968 Free PMC article.
-
Gene set analysis of SNP data: benefits, challenges, and future directions.Eur J Hum Genet. 2011 Aug;19(8):837-43. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.57. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21487444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene set analysis of genome-wide association studies: methodological issues and perspectives.Genomics. 2011 Jul;98(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2011.04.006. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21565265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Powerful Procedure for Pathway-Based Meta-analysis Using Summary Statistics Identifies 43 Pathways Associated with Type II Diabetes in European Populations.PLoS Genet. 2016 Jun 30;12(6):e1006122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006122. eCollection 2016 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27362418 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association meta-analysis on apolipoprotein A-IV concentrations.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Aug 15;25(16):3635-3646. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw211. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27412012 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies two loci associated with circulating osteoprotegerin levels.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Dec 15;23(24):6684-93. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu386. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 25080503 Free PMC article.
-
Powerful Tests for Multi-Marker Association Analysis Using Ensemble Learning.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 30;10(11):e0143489. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143489. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26619286 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Common Genetic Variants Influencing Spontaneous Dizygotic Twinning and Female Fertility.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 May 5;98(5):898-908. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.03.008. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27132594 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

