Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 regulates the function of interferon regulatory factor 7 by inducing its sumoylation
- PMID: 22951831
- PMCID: PMC3486478
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01407-12
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 regulates the function of interferon regulatory factor 7 by inducing its sumoylation
Abstract
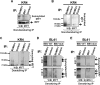
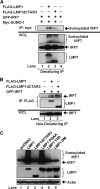
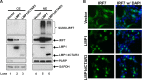
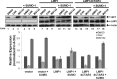
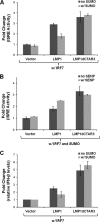
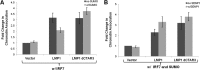
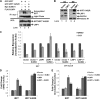
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) induces multiple signal transduction pathways during latent EBV infection via its C-terminal activating region 1 (CTAR1), CTAR2, and the less-studied CTAR3. One mechanism by which LMP1 regulates cellular activation is through the induction of protein posttranslational modifications, including phosphorylation and ubiquitination. We recently documented that LMP1 induces a third major protein modification by physically interacting with the SUMO-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 through CTAR3 and inducing the sumoylation of cellular proteins in latently infected cells. We have now identified a specific target of LMP1-induced sumoylation, interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7). We hypothesize that during EBV latency, LMP1 induces the sumoylation of IRF7, limiting its transcriptional activity and modulating the activation of innate immune responses. Our data show that endogenously sumoylated IRF7 is detected in latently infected EBV lymphoblastoid cell lines. LMP1 expression coincided with increased sumoylation of IRF7 in a CTAR3-dependent manner. Additional experiments show that LMP1 CTAR3-induced sumoylation regulates the expression and function of IRF7 by decreasing its turnover, increasing its nuclear retention, decreasing its DNA binding, and limiting its transcriptional activation. Finally, we identified that IRF7 is sumoylated at lysine 452. These data demonstrate that LMP1 CTAR3 does in fact function in intracellular signaling, leading to biologic effects. We propose that CTAR3 is an important signaling region of LMP1 that regulates protein function by sumoylation. We have shown specifically that LMP1 CTAR3, in cooperation with CTAR2, can limit the ability of IRF7 to induce innate immune responses by inducing the sumoylation of IRF7.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LMP1-Induced Sumoylation Influences the Maintenance of Epstein-Barr Virus Latency through KAP1.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7465-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00711-15. Epub 2015 May 6. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25948750 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) C-terminal-activating region 3 contributes to LMP1-mediated cellular migration via its interaction with Ubc9.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10144-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05035-11. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21795333 Free PMC article.
-
The A20 deubiquitinase activity negatively regulates LMP1 activation of IRF7.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(12):6130-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00364-10. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20392859 Free PMC article.
-
IRF7: activation, regulation, modification and function.Genes Immun. 2011 Sep;12(6):399-414. doi: 10.1038/gene.2011.21. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Genes Immun. 2011. PMID: 21490621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB and IRF7 pathway activation by Epstein-Barr virus Latent Membrane Protein 1.Viruses. 2013 Jun 21;5(6):1587-606. doi: 10.3390/v5061587. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23793113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential role of viral infection and B cells as a linker between innate and adaptive immune response in systemic lupus erythematosus.Immunol Res. 2021 Apr;69(2):196-204. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09186-4. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33786699
-
Human SUMOylation Pathway Is Critical for Influenza B Virus.Viruses. 2022 Feb 3;14(2):314. doi: 10.3390/v14020314. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215907 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein-1 Induces the Expression of SUMO-1 and SUMO-2/3 in LMP1-positive Lymphomas and Cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 18;9(1):208. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36312-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30659232 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin modification by SUMO-2/3 but not SUMO-1 prevents the epigenetic activation of key immune-related genes during Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus reactivation.BMC Genomics. 2013 Nov 23;14(1):824. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-824. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24267727 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Mediated Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 28;12(9):2441. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092441. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey D, O'Hare P. 2004. Characterization of the localization and proteolytic activity of the SUMO-specific protease, SENP1. J. Biol. Chem. 279:692–703 - PubMed
-
- Brennan P, Floettmann JE, Mehl A, Jones M, Rowe M. 2001. Mechanism of action of a novel latent membrane protein-1 dominant negative. J. Biol. Chem. 276:1195–1203 - PubMed
-
- Calender A, Cordier M, Billaud M, Lenoir GM. 1990. Modulation of cellular gene expression in B lymphoma cells following in vitro infection by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Int. J. Cancer 46:658–663 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

