Inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis by CDDO-Me in pancreatic cancer cells is ROS-dependent
- PMID: 22946344
- PMCID: PMC3846287
Inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis by CDDO-Me in pancreatic cancer cells is ROS-dependent
Abstract
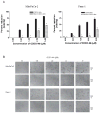
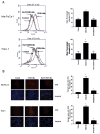
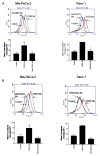
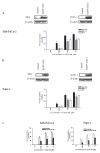
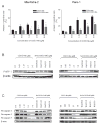
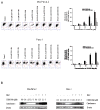
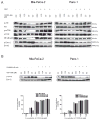
Oleanolic acid-derived synthetic triterpenoids are broad spectrum antiproliferative and antitumorigenic agents. In this study, we investigated the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in induction of apoptosis and inhibition of prosurvival Akt, NF-kappaB and mTOR signaling pro-teins by methyl-2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oate (CDDO-Me) in pancreatic cancer cells. Micromolar concentrations of CDDO-Me inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1 pancreatic cancer cells. Treatment with CDDO-Me caused the generation of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anion and pretreatment of cells with NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphylene iodonium (DPI) or respiratory chain complex 1 inhibitor rotenone prevented ROS generation. Pretreatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) or overexpression of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) or superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD-1) blocked the antiproliferative effects of CDDO-Me. Likewise, NAC prevented the induction of apoptosis (annexin V-FITC binding and cleavage of PARP-1 and procaspases-3,-8 and -9) and reversed the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and release of cytochrome c from mitochondria by CDDO-Me. CDDO-Me down-regulated p-Akt, p-mTOR and NF-kappaB (p65) but increased the activation of Erk1/2 and NAC blocked the modulation of these cell signaling proteins by CDDO-Me. Thus, the results of this study indicate that the antiproliferative and apoptosis inducing effects of CDDO-Me are mediated through a ROS-dependent mechanism and the role of ROS in modulation of signaling proteins by CDDO-Me warrants further investigation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ROS mediate proapoptotic and antisurvival activity of oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me in ovarian cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2013 Jan;33(1):215-21. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23267148 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of telomerase activity by oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me in pancreatic cancer cells is ROS-dependent.Molecules. 2013 Mar 13;18(3):3250-65. doi: 10.3390/molecules18033250. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 23486104 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through a ROS-dependent mechanism.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 1;79(3):350-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.09.006. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19782051 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of CDDO and CDDO-Me, Two Derivatives of Natural Triterpenoids.Molecules. 2019 Nov 13;24(22):4097. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224097. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unifying mechanisms of action of the anticancer activities of triterpenoids and synthetic analogs.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 Dec;12(10):1211-20. doi: 10.2174/187152012803833099. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22583404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical evidences toward the use of triterpenoid CDDO-Me for solid cancer prevention and treatment.Mol Cancer. 2014 Feb 20;13:30. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-30. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24552536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of natural products in revealing NRF2 function.Nat Prod Rep. 2020 Jun 1;37(6):797-826. doi: 10.1039/c9np00061e. Epub 2020 May 13. Nat Prod Rep. 2020. PMID: 32400766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laminarin Attenuates ROS-Mediated Cell Migration and Invasiveness through Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Pancreatic Cancer Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;11(9):1714. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091714. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139787 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinantly tailored β-defensin that displays intensive macropinocytosis-mediated uptake exerting potent efficacy against K-Ras mutant pancreatic cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58418-58434. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11170. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27517152 Free PMC article.
-
[6]-Gingerol inhibits de novo fatty acid synthesis and carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 activity which triggers apoptosis in HepG2.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Mar 15;5(4):1319-36. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26101700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2004;363:1049–57. - PubMed
-
- Pino SM, Xiong HQ, McConkey D, Abbruzzese JL. Novel therapies for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Curr Oncol Rep 2004. 2004;6:199–206. - PubMed
-
- Mulcahy MF, Wahl AO, Small W., Jr The current status of combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy for locally advanced or resected pancreas cancer. J Nat Compr Netw. 2005;3:637–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
