Therapeutic efficacy by targeting correction of Notch1-induced aberrants in uveal tumors
- PMID: 22937170
- PMCID: PMC3429424
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044301
Therapeutic efficacy by targeting correction of Notch1-induced aberrants in uveal tumors
Abstract
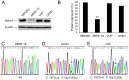
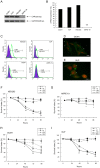
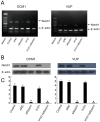
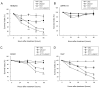
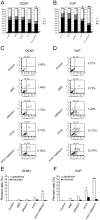
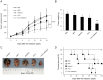
There is a need for more effective treatments for uveal melanoma. The recombinant oncolytic adenovirus H101 replicates specifically in p53-depleted tumor cells, and has been approved for use by the Chinese State Food and Drug Administration. However, this treatment is associated with subsequent remission. Transfection of uveal melanoma cells with a small interfering RNA against Notch1 (siNotch1) effectively suppressed Notch1 expression, resulting in significant cell growth inhibition when combined with H101 treatment. Combined treatment with siNotch1 and H101 (H101-Notch1-siRNA) greatly enhanced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in vitro as compared to treatment with H101 or siNotch1 alone. For in vivo treatments, the combined treatment of siNotch1 and H101 showed remarkable tumor growth inhibition and prolonged mouse survival in the OCM1 xenograft model. We predict that Notch pathway deregulation could be a feature of uveal melanoma, and could be a therapeutic target, especially if p53 is concurrently targeted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The oncolytic virus H101 combined with GNAQ siRNA-mediated knockdown reduces uveal melanoma cell viability.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):5766-5776. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27863. Epub 2018 Oct 15. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30320917
-
Recombinant oncolytic adenovirus H101 combined with siBCL2: cytotoxic effect on uveal melanoma cell lines.Br J Ophthalmol. 2012 Oct;96(10):1331-8. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2011-301470. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22843987
-
A novel anticancer therapy that simultaneously targets aberrant p53 and Notch activities in tumors.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046627. Epub 2012 Oct 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23071601 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in uveal melanoma treatment.Med Res Rev. 2017 Nov;37(6):1350-1372. doi: 10.1002/med.21460. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Med Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28759124 Review.
-
Update on Metastatic Uveal Melanoma: Progress and Challenges.BioDrugs. 2016 Jun;30(3):161-72. doi: 10.1007/s40259-016-0167-4. BioDrugs. 2016. PMID: 27000042 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic Virotherapy: From Bench to Bedside.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 26;9:790150. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.790150. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34901031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus-based strategies enhance antitumor capability through p53-mediated downregulation of MGMT in uveal melanoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Mar 4;18(3):194-199. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1294287. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28278076 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of uveal melanoma.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017 Mar;36(1):109-140. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9663-3. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017. PMID: 28229253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-targeting TRAIL expression mediated by miRNA response elements suppressed growth of uveal melanoma cells.Mol Oncol. 2013 Dec;7(6):1043-55. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24001901 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Bax and Bcl-2 in gemcitabine-mediated cytotoxicity in uveal melanoma cells.Tumour Biol. 2014 Feb;35(2):1169-75. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1156-6. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24014050
References
-
- Egan KM, Seddon JM, Glynn RJ, Gragoudas ES, Albert DM (1988) Epidemiologic aspects of uveal melanoma. Surv Ophthalmol 32: 239–251. - PubMed
-
- Inskip PD, Devesa SS, Fraumeni JF Jr (2003) Trends in the incidence of ocular melanoma in the United States, 1974–1998. Cancer Causes Control 14: 251–257. - PubMed
-
- Damato B, Coupland SE (2009) Genomic typing of uveal melanoma. Arch Ophthalmol 127: 113–114; author reply 114–115. - PubMed
-
- Kujala E, Tuomaala S, Eskelin S, Kivela T (2009) Mortality after uveal and conjunctival melanoma: which tumour is more deadly? Acta Ophthalmol 87: 149–153. - PubMed
-
- Triozzi PL, Eng C, Singh AD (2008) Targeted therapy for uveal melanoma. Cancer Treat Rev 34: 247–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

