Epigenetic therapy with 3-deazaneplanocin A, an inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase EZH2, inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 22925699
- PMCID: PMC3472089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.08.003
Epigenetic therapy with 3-deazaneplanocin A, an inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase EZH2, inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
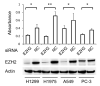
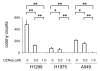
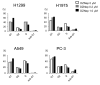
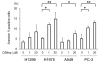
EZH2 (enhancer of zeste homolog 2) is the catalytic subunit of PRC2 (polycomb repressive complex 2), which mediates histone methyltransferase activity and functions as transcriptional repressor involved in gene silencing. EZH2 is involved in malignant transformation and biological aggressiveness of several human malignancies. We previously demonstrated that non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) also overexpress EZH2 and that high expression of EZH2 correlates with poor prognosis. Growing evidence indicates that EZH2 may be an appropriate therapeutic target in malignancies, including NSCLCs. Recently, an S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase inhibitor, 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), has been shown to deplete and inhibit EZH2. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of DZNep in NSCLC cells. Knockdown of EZH2 by small-interfering RNA (siRNA) resulted in decreased growth of four NSCLC cell lines. MTT assays demonstrated that DZNep treatment resulted in dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation in the NSCLC cell lines with a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) ranging from 0.08 to 0.24 μM. Immortalized but non-cancerous bronchial epithelial and fibroblast cell lines were less sensitive to DZNep than the NSCLC cell lines. Soft agarose assays demonstrated that anchorage-independent growth was also reduced in all three NSCLC cell lines that were evaluated using this assay. Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated that DZNep induced apoptosis and G1 cell cycle arrest in NSCLC cells, which was partially associated with cyclin A decrease and p27(Kip1) accumulation. DZNep depleted cellular levels of EZH2 and inhibited the associated histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation. These results indicated that an epigenetic therapy that pharmacologically targets EZH2 via DZNep may constitute a novel approach to treatment of NSCLCs.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic therapy with the histone methyltransferase EZH2 inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin A inhibits the growth of cholangiocarcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2014 Feb;31(2):983-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2922. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24337160
-
Combined inhibition of EZH2 and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2016 Jul;107(7):955-62. doi: 10.1111/cas.12957. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27116120 Free PMC article.
-
Superior efficacy of a combined epigenetic therapy against human mantle cell lymphoma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Nov 15;18(22):6227-38. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0873. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22932665 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EZH2 and PRC2 dependence as novel anticancer therapy.Exp Hematol. 2015 Aug;43(8):698-712. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 28. Exp Hematol. 2015. PMID: 26027790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of cancer stem cells by inhibitors of DNA and histone methylation.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(8):1031-43. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2015.1051220. Epub 2015 May 25. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26004134 Review.
Cited by
-
Polycomb repressive 2 complex-Molecular mechanisms of function.Protein Sci. 2019 Aug;28(8):1387-1399. doi: 10.1002/pro.3647. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Protein Sci. 2019. PMID: 31095801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A large scale mass spectrometry-based histone screening for assessing epigenetic developmental toxicity.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 24;12(1):1256. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05268-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35075221 Free PMC article.
-
Can we better predict the biologic behavior of incidental IPMN? A comprehensive analysis of molecular diagnostics and biomarkers in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2018 Mar;403(2):151-194. doi: 10.1007/s00423-017-1644-z. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2018. PMID: 29218397 Review.
-
Lung Cancer Therapy Targeting Histone Methylation: Opportunities and Challenges.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018 Jun 20;16:211-223. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.06.001. eCollection 2018. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 30002791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The KDM2B- let-7b -EZH2 axis in myelodysplastic syndromes as a target for combined epigenetic therapy.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 16;9(9):e107817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107817. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25225797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM. Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2001;2:533–543. - PubMed
-
- Ringrose L, Paro R. Epigenetic regulation of cellular memory by the Polycomb and Trithorax group proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:413–443. - PubMed
-
- Sparmann A, van Lohuizen M. Polycomb silencers control cell fate, development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:846–856. - PubMed
-
- Cao R, Zhang Y. The functions of E(Z)/EZH2-mediated methylation of lysine 27 in histone H3. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14:155–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

