Nutrient sensor-mediated programmed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in low birthweight offspring
- PMID: 22921094
- PMCID: PMC4234167
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2012.07.033
Nutrient sensor-mediated programmed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in low birthweight offspring
Abstract
Objective: We hypothesized that gestationally programmed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in low-birthweight offspring is mediated through nutrient sensors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+-dependent histone deacetylase (SIRT1) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK).
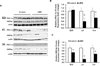
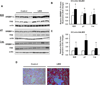
Study design: Pregnant dams received ad libitum food or were 50% food restricted from pregnancy days 10-21 to produce control and low-birthweight newborn offspring, respectively. All pups were nursed by control dams and weaned to ad libitum feed. We determined hepatic SIRT1 and AMPK activities and protein expression of lipid targets in low-birthweight and control fetuses, newborns, and adult offspring (3 months).
Results: Low-birthweight fetuses demonstrated increased prenatal hepatic SIRT1 activity, although with increased lipogenesis. After birth, low-birthweight newborn offspring undergo postnatal suppression of hepatic SIRT1 and AMPK activities in conjunction with increased lipogenesis, decreased lipolysis, and increased fat stores.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that undernutrition stress in utero may program hepatic nutrient sensors to perceive normal postnatal nutrition as a state of nutrient excess with the induction of hepatic lipid storage.
Copyright © 2012 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: None of the authors have a conflict of interest
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetics of programmed obesity: alteration in IUGR rat hepatic IGF1 mRNA expression and histone structure in rapid vs. delayed postnatal catch-up growth.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):G1023-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00052.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20813916 Free PMC article.
-
Early onset of fatty liver in growth-restricted rat fetuses and newborns.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2011 Dec;51(4):167-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-4520.2011.00336.x. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2011. PMID: 22103455 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in programmed hepatic lipid dysregulation and inflammation in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Sep;199(3):271.e1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.05.022. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008. PMID: 18667178 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed obesity in intrauterine growth-restricted newborns: modulation by newborn nutrition.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005 Jan;288(1):R91-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00340.2004. Epub 2004 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15297266
-
Emerging roles of SIRT1 in fatty liver diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Jul 6;13(7):852-867. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.19370. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28808418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-199a-5p regulates sirtuin1 and PI3K in the rat hippocampus with intrauterine growth restriction.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 14;8(1):13813. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32189-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30217997 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dimethylglycine sodium salt supplementation on growth performance, hepatic antioxidant capacity, and mitochondria-related gene expression in weanling piglets born with low birth weight1.J Anim Sci. 2018 Sep 7;96(9):3791-3803. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky233. J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 29931075 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial role in the neonatal predisposition to developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.J Clin Invest. 2018 Aug 31;128(9):3692-3703. doi: 10.1172/JCI120846. Epub 2018 Aug 31. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30168806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Undernourishment in utero Primes Hepatic Steatosis in Adult Mice Offspring on an Obesogenic Diet; Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 19;5:16867. doi: 10.1038/srep16867. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26581663 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition and Developmental Origins of Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 29;15(19):4207. doi: 10.3390/nu15194207. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Falck-Ytter Y, Younossi ZM, Marchesini G, McCullough AJ. Clinical features and natural history of nonalcoholic steatosis syndromes. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21(1):17–26. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Shimano H, Nakagawa Y, Ide T, Yahagi N, Matsuzaka T, et al. SREBP-1 interacts with hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha and interferes with PGC-1 recruitment to suppress hepatic gluconeogenic genes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(13):12027–12035. - PubMed
-
- Blander G, Guarente L. The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:417–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

