Faecal pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 for colorectal cancer screening: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 22912551
- PMCID: PMC3419997
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.4004
Faecal pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 for colorectal cancer screening: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To present a critical discussion of the efficacy of the faecal pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 (faecal M2-PK) test for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening based on the currently available studies.
Methods: A literature search in PubMed and Embase was conducted using the following search terms: fecal Tumor M2-PK, faecal Tumour M2-PK, fecal M2-PK, faecal M2-PK, fecal pyruvate kinase, faecal pyruvate kinase, pyruvate kinase stool and M2-PK stool.
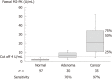
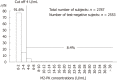
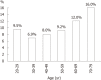
Results: Stool samples from 704 patients with CRC and from 11 412 healthy subjects have been investigated for faecal M2-PK concentrations in seventeen independent studies. The mean faecal M2-PK sensitivity was 80.3%; the specificity was 95.2%. Four studies compared faecal M2-PK head-to-head with guaiac-based faecal occult blood test (gFOBT). Faecal M2-PK demonstrated a sensitivity of 81.1%, whereas the gFOBT detected only 36.9% of the CRCs. Eight independent studies investigated the sensitivity of faecal M2-PK for adenoma (n = 554), with the following sensitivities: adenoma < 1 cm in diameter: 25%; adenoma > 1 cm: 44%; adenoma of unspecified diameter: 51%. In a direct comparison with gFOBT of adenoma > 1 cm in diameter, 47% tested positive with the faecal M2-PK test, whereas the gFOBT detected only 27%.
Conclusion: We recommend faecal M2-PK as a routine test for CRC screening. Faecal M2-PK closes a gap in clinical practice because it detects bleeding and non-bleeding tumors and adenoma with high sensitivity and specificity.
Keywords: Adenoma; Colorectal cancer; Colorectal cancer screening; Faecal occult blood; Faecal pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2; Polyps; Stool.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Usefulness of a Novel Screening Kit for Colorectal Cancer Using the Immunochromatographic Fecal Tumor M2 Pyruvate Kinase Test.Gut Liver. 2015 Sep 23;9(5):641-8. doi: 10.5009/gnl13457. Gut Liver. 2015. PMID: 25473070 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of faecal protein biomarkers' diagnostic accuracy for colorectal advanced neoplasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 16;12(1):2623. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06689-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35173276 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of faecal M2-PK and FIT in a population-based bowel cancer screening cohort.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 May;26(5):514-8. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000025. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24699725
-
Tumour M2-pyruvate kinase: a gastrointestinal cancer marker.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Mar;19(3):265-76. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3280102f78. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17301655 Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of pyruvate kinase M2 isoenzymatic assay in diagnosing colorectal cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2015 Feb 13;13:48. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0446-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25888768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Usefulness of a Novel Screening Kit for Colorectal Cancer Using the Immunochromatographic Fecal Tumor M2 Pyruvate Kinase Test.Gut Liver. 2015 Sep 23;9(5):641-8. doi: 10.5009/gnl13457. Gut Liver. 2015. PMID: 25473070 Free PMC article.
-
Faecal occult blood testing for colorectal cancer screening: the past or the future.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2015 Feb;17(2):428. doi: 10.1007/s11894-015-0428-2. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25673567 Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Five Different Fecal Markers for the Detection of Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions of the Colorectum.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:2492081. doi: 10.1155/2016/2492081. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27413251 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of genes from feces correlated with colorectal cancer progression.Oncol Lett. 2016 Nov;12(5):3378-3384. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5069. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27900008 Free PMC article.
-
Early detection of colorectal cancer: from conventional methods to novel biomarkers.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Feb;142(2):341-51. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-1928-z. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 25687380 Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Parkin DM, Steliarova-Foucher E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:765–781. - PubMed
-
- Garcia M, Jemal A, Ward EM, Center MM, Hao Y, Siegel RL, Thun MJ. Global cancer facts and figures 2007. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2007.
-
- Altenhof L. Wissenschaftliche Begleitung der Früherkennungs-Koloskopie 6. Jahresberich. 2008 Available from: http://www.berliner-gastroenterologen.de/uploads/media/6.Jahresbericht_Z....
-
- Allison JE, Tekawa IS, Ransom LJ, Adrain AL. A comparison of fecal occult-blood tests for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, Turnbull BA, Ross ME. Fecal DNA versus fecal occult blood for colorectal-cancer screening in an average-risk population. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2704–2714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

