The slicing activity of miRNA-specific Argonautes is essential for the miRNA pathway in C. elegans
- PMID: 22904066
- PMCID: PMC3488219
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks748
The slicing activity of miRNA-specific Argonautes is essential for the miRNA pathway in C. elegans
Abstract
Among the set of Argonautes proteins encoded by metazoan genomes, some have conserved amino acids important for catalytic or slicing activity. The functional significance of these residues in microRNA (miRNA)-specific Argonautes in animals is still unclear since miRNAs do not induce site-specific cleavage of targeted messenger RNAs (mRNAs), unlike small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Here, we report that miRNA-specific ALG-1 and ALG-2 Argonautes from Caenorhabditis elegans possess the slicing activity normally implicated in the siRNA-silencing pathway. We also find that ALG-1/2 can bind and use a Dicer-processed miRNA duplex to target mRNAs, suggesting an ability to displace RNA strands. Importantly, the slicing activity of ALG-1 or ALG-2 is essential for the miRNA pathway in vivo, as shown by the accumulation of truncated miRNA precursors and altered miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) formation. Taken together, our data demonstrate that the slicing activity of Argonautes contributes to a new and unexpected step in the canonical miRNA pathway that occurs prior to miRISC loading in animals.
Figures
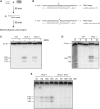
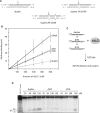
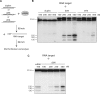
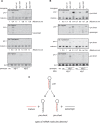
Similar articles
-
Defining the contribution of microRNA-specific Argonautes with slicer capability in animals.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 22;52(9):5002-5015. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae173. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38477356 Free PMC article.
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans Argonautes ALG-1 and ALG-2: almost identical yet different.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:189-94. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.035. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381296
-
TEG-1 CD2BP2 controls miRNA levels by regulating miRISC stability in C. elegans and human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 17;45(3):1488-1500. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw836. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28180320 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi pathway in C. elegans: the argonautes and collaborators.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;320:21-36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75157-1_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18268838 Review.
-
siRNA and miRNA: an insight into RISCs.Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 Feb;30(2):106-14. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.12.007. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15691656 Review.
Cited by
-
A new role for the GARP complex in microRNA-mediated gene regulation.PLoS Genet. 2013 Nov;9(11):e1003961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003961. Epub 2013 Nov 7. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24244204 Free PMC article.
-
Nematode endogenous small RNA pathways.Worm. 2014 Mar 5;3:e28234. doi: 10.4161/worm.28234. eCollection 2014. Worm. 2014. PMID: 25340013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the mitochondrial microRNA import pathway through Polynucleotide Phosphorylase (PNPase).J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Sep;110:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.06.012. Epub 2017 Jul 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28709769 Free PMC article.
-
New role for DCR-1/dicer in Caenorhabditis elegans innate immunity against the highly virulent bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis DB27.Infect Immun. 2013 Oct;81(10):3942-57. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00700-13. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23918784 Free PMC article.
-
RACK-1 regulates let-7 microRNA expression and terminal cell differentiation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(12):1995-2009. doi: 10.4161/cc.29017. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24776851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009;10:126–139. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G, Simard MJ. Argonaute proteins: key players in RNA silencing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008;9:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Lingel A, Simon B, Izaurralde E, Sattler M. Nucleic acid 3'-end recognition by the Argonaute2 PAZ domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:576–577. - PubMed
-
- Frank F, Sonenberg N, Nagar B. Structural basis for 5'-nucleotide base-specific recognition of guide RNA by human AGO2. Nature. 2010;465:818–822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

