K-ATP channels in dopamine substantia nigra neurons control bursting and novelty-induced exploration
- PMID: 22902720
- PMCID: PMC4242970
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3185
K-ATP channels in dopamine substantia nigra neurons control bursting and novelty-induced exploration
Abstract
Phasic activation of the dopamine (DA) midbrain system in response to unexpected reward or novelty is critical for adaptive behavioral strategies. This activation of DA midbrain neurons occurs via a synaptically triggered switch from low-frequency background spiking to transient high-frequency burst firing. We found that, in medial DA neurons of the substantia nigra (SN), activity of ATP-sensitive potassium (K-ATP) channels enabled NMDA-mediated bursting in vitro as well as spontaneous in vivo burst firing in anesthetized mice. Cell-selective silencing of K-ATP channel activity in medial SN DA neurons revealed that their K-ATP channel-gated burst firing was crucial for novelty-dependent exploratory behavior. We also detected a transcriptional upregulation of K-ATP channel and NMDA receptor subunits, as well as high in vivo burst firing, in surviving SN DA neurons from Parkinson's disease patients, suggesting that burst-gating K-ATP channel function in DA neurons affects phenotypes in both disease and health.
Figures




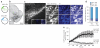
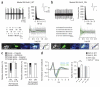
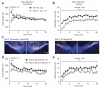
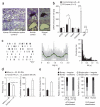
Comment in
-
Bursting for exploration.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Sep;15(9):1178-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.3198. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22929910 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Calcium dynamics control K-ATP channel-mediated bursting in substantia nigra dopamine neurons: a combined experimental and modeling study.J Neurophysiol. 2018 Jan 1;119(1):84-95. doi: 10.1152/jn.00351.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 4. J Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 28978764 Free PMC article.
-
Cav1.3 channels control D2-autoreceptor responses via NCS-1 in substantia nigra dopamine neurons.Brain. 2014 Aug;137(Pt 8):2287-302. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu131. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Brain. 2014. PMID: 24934288 Free PMC article.
-
K-ATP channels promote the differential degeneration of dopaminergic midbrain neurons.Nat Neurosci. 2005 Dec;8(12):1742-51. doi: 10.1038/nn1570. Epub 2005 Nov 20. Nat Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16299504
-
Dissecting the diversity of midbrain dopamine neurons.Trends Neurosci. 2013 Jun;36(6):336-42. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Trends Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23582338 Review.
-
Converging roles of ion channels, calcium, metabolic stress, and activity pattern of Substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons in health and Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 1(Suppl Suppl 1):156-178. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13572. Epub 2016 Mar 23. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26865375 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterogeneity in Dopamine Neuron Synaptic Actions Across the Striatum and Its Relevance for Schizophrenia.Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 1;81(1):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27692238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalein attenuates rotenone-induced SH-SY5Y cell apoptosis through binding to SUR1 and activating ATP-sensitive potassium channels.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Mar;45(3):480-489. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01187-3. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37993535
-
Kir6.2-deficient mice develop somatosensory dysfunction and axonal loss in the peripheral nerves.iScience. 2021 Dec 11;25(1):103609. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103609. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35005553 Free PMC article.
-
A neurocomputational account of reward and novelty processing and effects of psychostimulants in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.Brain. 2018 May 1;141(5):1545-1557. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy048. Brain. 2018. PMID: 29547978 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sequential Application of Discrete Topographical Patterns Enhances Derivation of Functional Mesencephalic Dopaminergic Neurons from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 22;8(1):9567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27653-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29934644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schultz W. Multiple dopamine functions at different time courses. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007;30:259–288. - PubMed
-
- Lammel S, et al. Unique properties of mesoprefrontal neurons within a dual mesocorticolimbic dopamine system. Neuron. 2008;57:760–773. - PubMed
-
- Krebs RM, Heipertz D, Schuetze H, Duzel E. Novelty increases the mesolimbic functional connectivity of the substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area (SN/VTA) during reward anticipation: Evidence from high-resolution fMRI. Neuroimage. 2011;58:647–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

