Degradation of host microRNAs by poxvirus poly(A) polymerase reveals terminal RNA methylation as a protective antiviral mechanism
- PMID: 22901540
- PMCID: PMC3782087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.05.019
Degradation of host microRNAs by poxvirus poly(A) polymerase reveals terminal RNA methylation as a protective antiviral mechanism
Abstract
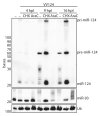
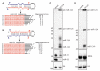
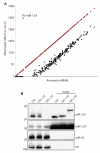
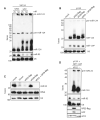
The life cycle of several viruses involves host or virally encoded small noncoding RNAs, which play important roles in posttranscriptional regulation. Small noncoding RNAs include microRNAs (miRNAs), which modulate the transcriptome, and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which are involved in pathogen defense in plants, worms, and insects. We show that insect and mammalian poxviruses induce the degradation of host miRNAs. The virally encoded poly(A) polymerase, which polyadenylates viral transcripts, also mediates 3' polyadenylation of host miRNAs, resulting in their degradation by the host machinery. In contrast, siRNAs, which are protected by 2'O-methylation (2'OMe), were not targeted by poxviruses. These findings suggest that poxviruses may degrade host miRNAs to promote replication and that virus-mediated small RNA degradation likely contributed to 2'OMe evolution.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Translational control during poxvirus infection.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Mar;10(2):e1515. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1515. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30381906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poxviruses and the evolution of host range and virulence.Infect Genet Evol. 2014 Jan;21:15-40. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.10.014. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Infect Genet Evol. 2014. PMID: 24161410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific miRNA stabilization by Gld2-catalyzed monoadenylation.Cell Rep. 2012 Dec 27;2(6):1537-45. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.10.023. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 23200856 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress on host range factors and their mechanisms of poxvirus].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2013 Nov;29(6):655-61. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 24520773 Review. Chinese.
-
Use of functional genomics to understand replication deficient poxvirus-host interactions.Virus Res. 2016 May 2;216:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 26519757 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Analysis of MicroRNAs in Vaccinia virus Infection Reveals Diversity in Their Susceptibility to Modification and Suppression.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 10;10(7):e0131787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131787. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26161560 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral RNAi in Insects and Mammals: Parallels and Differences.Viruses. 2019 May 16;11(5):448. doi: 10.3390/v11050448. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31100912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA virus building blocks-miRNAs not included.PLoS Pathog. 2018 May 31;14(5):e1006963. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006963. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29852025 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Computationally predicted SARS-COV-2 encoded microRNAs target NFKB, JAK/STAT and TGFB signaling pathways.Gene Rep. 2021 Mar;22:101012. doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2020.101012. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Gene Rep. 2021. PMID: 33398248 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and consequences of mRNA destabilization during viral infections.Virol J. 2024 Feb 6;21(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02305-1. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38321453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

