Bacterial pathogens commandeer Rab GTPases to establish intracellular niches
- PMID: 22901006
- PMCID: PMC3530015
- DOI: 10.1111/tra.12000
Bacterial pathogens commandeer Rab GTPases to establish intracellular niches
Abstract
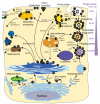
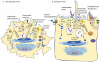
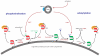
Intracellular bacterial pathogens deploy virulence factors termed effectors to inhibit degradation by host cells and to establish intracellular niches where growth and differentiation take place. Here, we describe mechanisms by which human bacterial pathogens (including Chlamydiae; Coxiella burnetii; Helicobacter pylori; Legionella pneumophila; Listeria monocytogenes; Mycobacteria; Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella enterica) modulate endocytic and exocytic Rab GTPases in order to thrive in host cells. Host cell Rab GTPases are critical for intracellular transport following pathogen phagocytosis or endocytosis. At the molecular level bacterial effectors hijack Rab protein function to: evade degradation, direct transport to particular intracellular locations and monopolize host vesicles carrying molecules that are needed for a stable niche and/or bacterial growth and differentiation. Bacterial effectors may serve as specific receptors for Rab GTPases or as enzymes that post-translationally modify Rab proteins or endosomal membrane lipids required for Rab function. Emerging data indicate that bacterial effector expression is temporally and spatially regulated and multiple virulence factors may act concertedly to usurp Rab GTPase function, alter signaling and ensure niche establishment and intracellular bacterial growth, making this field an exciting area for further study.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Taking control: Hijacking of Rab GTPases by intracellular bacterial pathogens.Small GTPases. 2018 Mar 4;9(1-2):182-191. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1336192. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 28632996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manipulation of rab GTPase function by intracellular bacterial pathogens.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Dec;71(4):636-52. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00023-07. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007. PMID: 18063721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The recycling endosome and bacterial pathogens.Cell Microbiol. 2018 Jul;20(7):e12857. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12857. Epub 2018 May 30. Cell Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29748997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Rab GTPases in the transport of vacuoles containing Legionella pneumophila and Coxiella burnetii.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Dec 1;40(6):1353-9. doi: 10.1042/BST20120167. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 23176480 Review.
-
Functional Divergence of the Paralog Salmonella Effector Proteins SopD and SopD2 and Their Contributions to Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 10;25(8):4191. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084191. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Group A Streptococcus Induces LAPosomes via SLO/β1 Integrin/NOX2/ROS Pathway in Endothelial Cells That Are Ineffective in Bacterial Killing and Suppress Xenophagy.mBio. 2019 Oct 1;10(5):e02148-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02148-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31575768 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition of Rab11 and Rab11-Fip2-A novel strategy for Chlamydia pneumoniae early survival.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Aug 7;13(8):e1006556. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006556. eCollection 2017 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28787457 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic Membrane Protein 17G of Chlamydia psittaci Mediated the Binding and Invasion of Bacteria to Host Cells by Interacting and Activating EGFR of the Host.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 31;12:818487. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.818487. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35173712 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii Plasmid Effector B Promotes LC3-II Accumulation and Contributes To Bacterial Virulence in a SCID Mouse Model.Infect Immun. 2022 Jun 16;90(6):e0001622. doi: 10.1128/iai.00016-22. Epub 2022 May 19. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 35587202 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role(s) of phagosomal Rab GTPases.Small GTPases. 2013 Jul-Sep;4(3):148-58. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.25604. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Small GTPases. 2013. PMID: 24088602 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ingmundson A, Delprato A, Lambright DG, Roy CR. Legionella pneumophila proteins that regulate Rab1 membrane cycling. Nature. 2007;450:365–369. - PubMed
-
- Muller MP, Peters H, Blumer J, Blankenfeldt W, Goody RS, Itzen A. The Legionella effector protein DrrA AMPylates the membrane traffic regulator Rab1b. Science. 2010;329:946–949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

