Targeted disruption of heparan sulfate interaction with hepatocyte and vascular endothelial growth factors blocks normal and oncogenic signaling
- PMID: 22897854
- PMCID: PMC3422512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.06.029
Targeted disruption of heparan sulfate interaction with hepatocyte and vascular endothelial growth factors blocks normal and oncogenic signaling
Abstract
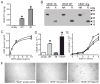
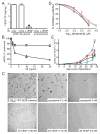
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) regulate normal development and homeostasis and drive disease progression in many forms of cancer. Both proteins signal by binding to receptor tyrosine kinases and heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycans on target cell surfaces. Basic residues comprising the primary HS binding sites on HGF and VEGF provide similar surface charge distributions without underlying structural similarity. Combining three acidic amino acid substitutions in these sites in the HGF isoform NK1 or the VEGF isoform VEGF165 transformed each into potent, selective competitive antagonists of their respective normal and oncogenic signaling pathways. Our findings illustrate the importance of HS in growth factor driven cancer progression and reveal an efficient strategy for therapeutic antagonist development.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dissociation of heparan sulfate and receptor binding domains of hepatocyte growth factor reveals that heparan sulfate-c-met interaction facilitates signaling.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 31;276(35):32977-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105486200. Epub 2001 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11435444
-
Isolation and Characterization of a Chinese Hamster Ovary Heparan Sulfate Cell Mutant Defective in Both Met Receptor Binding and Hepatocyte Growth Factor NK1/Met Signaling.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(4):1480-1491. doi: 10.1159/000492258. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30107380
-
Heparin binding and oligomerization of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor isoforms. Heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan requirement for Met binding and signaling.J Biol Chem. 1997 Apr 4;272(14):9457-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.14.9457. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9083085
-
Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor/Met pathway in cancer.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Aug 15;45(4):855-870. doi: 10.1042/BST20160132. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28673936 Review.
-
Signalling by HGF/SF and Met: the role of heparan sulphate co-receptors.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Jun;34(Pt 3):414-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0340414. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16709175 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression array analysis of the hepatocyte growth factor invasive program.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015 Oct;32(7):659-76. doi: 10.1007/s10585-015-9735-0. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015. PMID: 26231668 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback regulation of RTK signaling in development.Dev Biol. 2019 Mar 1;447(1):71-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.017. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29079424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor and Plasma Met Levels in Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 14;11(6):e0157130. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157130. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27300295 Free PMC article.
-
MET Inhibition in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2016 Jun 18;7(10):1205-14. doi: 10.7150/jca.14604. eCollection 2016. J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27390595 Free PMC article.
-
A potential target for liver cancer management, lysophosphatidic acid receptor 6 (LPAR6), is transcriptionally up-regulated by the NCOA3 coactivator.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 7;295(6):1474-1488. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009899. Epub 2019 Dec 30. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31914406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appleton BA, Wu P, Maloney J, Yin J, Liang WC, Stawicki S, Mortara K, Bowman KK, Elliott JM, Desmarais W, Bazan JF, Bagri A, Tessier-Lavigne M, Koch AW, Wu Y, Watts RJ, Wiesmann C. Structural studies of neuropilin/antibody complexes provide insights into semaphorin and VEGF binding. EMBO Journal. 2007;26:4902–4912. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Backer MV, Gaynutdinov TI, Patel V, Bandyopadhyaya AK, Thirumamagal BT, Tjarks W, Barth RF, Claffey K, Backer JM. Vascular endothelial growth factor selectively targets boronated dendrimers to tumor vasculature. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2005;4:1423–1429. - PubMed
-
- Boccaccio C, Comoglio PM. Invasive growth: a MET-driven genetic programme for cancer and stem cells. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2006;6:637–645. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Ng YS, Nuyens D, Theilmeier G, Brusselmans K, Cornelissen I, Ehler E, Kakkar VV, Stalmans I, Mattot V, et al. Impaired myocardial angiogenesis and ischemic cardiomyopathy in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF164 and VEGF188. Nature Medicine. 1999;5:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Castagnino P, Lorenzi MV, Yeh J, Breckenridge D, Sakata H, Munz B, Werner S, Bottaro DP. Neu differentiation factor/heregulin induction by hepatocyte and keratinocyte growth factors. Oncogene. 2000;19:640–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

