Genome wide identification of promoter binding sites for H4K12ac in human sperm and its relevance for early embryonic development
- PMID: 22894908
- PMCID: PMC3466190
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.21556
Genome wide identification of promoter binding sites for H4K12ac in human sperm and its relevance for early embryonic development
Abstract
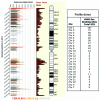
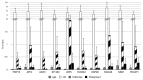
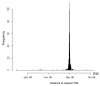
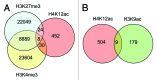
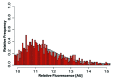
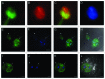
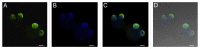
Sperm chromatin reveals two characteristic features in that protamines are the predominant nuclear proteins and remaining histones are highly acetylated. Histone H4 acetylated at lysine 12 (H4K12ac) is localized in the post-acrosomal region, while protamine-1 is present within the whole nucleus. Chromatin immunoprecipitation in combination with promoter array analysis allowed genome-wide identification of H4K12ac binding sites. Previously, we reported enrichment of H4K12ac at CTCF binding sites and promoters of genes involved in developmental processes. Here, we demonstrate that H4K12ac is enriched predominantly between ± 2 kb from the transcription start site. In addition, we identified developmentally relevant H4K12ac-associated promoters with high expression levels of their transcripts stored in mature sperm. The highest expressed mRNA codes for testis-specific PHD finger protein-7 (PHF7), suggesting an activating role of H4K12ac in the regulatory elements of this gene. H4K12ac-associated genes revealed a weak correlation with genes expressed at 4-cell stage human embryos, while 23 H4K12ac-associated genes were activated in 8-cell embryo and 39 in the blastocyst. Genes activated in 4-cell embryos are involved in gene expression, histone fold and DNA-dependent transcription, while genes expressed in the blastocyst were classified as involved in developmental processes. Immunofluorescence staining detected H4K12ac from the murine male pronucleus to early stages of embryogenesis. Aberrant histone acetylation within developmentally important gene promoters in infertile men may reflect insufficient sperm chromatin compaction, which may result in inappropriate transfer of epigenetic information to the oocyte.
Figures

Comment in
-
Intriguing H3K12ac localization in sperm chromatin: a record or a plan?Epigenomics. 2013 Feb;5(1):21-2. doi: 10.2217/epi.12.79. Epigenomics. 2013. PMID: 23414315 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Methylation analysis of histone H4K12ac-associated promoters in sperm of healthy donors and subfertile patients.Clin Epigenetics. 2015 Mar 19;7(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13148-015-0058-4. eCollection 2015. Clin Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25806092 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis identifies changes in histone retention and epigenetic modifications at developmental and imprinted gene loci in the sperm of infertile men.Hum Reprod. 2011 Sep;26(9):2558-69. doi: 10.1093/humrep/der192. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Hum Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21685136 Free PMC article.
-
H4K12ac is regulated by estrogen receptor-alpha and is associated with BRD4 function and inducible transcription.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 30;6(9):7305-17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3439. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25788266 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of human sperm proteins to the development and epigenome of the preimplantation embryo.Hum Reprod Update. 2018 Sep 1;24(5):535-555. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy017. Hum Reprod Update. 2018. PMID: 29800303 Review.
-
Chromatin in early mammalian embryos: achieving the pluripotent state.Differentiation. 2008 Jan;76(1):3-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2007.00247.x. Epub 2007 Dec 17. Differentiation. 2008. PMID: 18093226 Review.
Cited by
-
Parental competition for the regulators of chromatin dynamics in mouse zygotes.Commun Biol. 2022 Jul 14;5(1):699. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03623-2. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35835981 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear reprogramming of sperm and somatic nuclei in eggs and oocytes.Reprod Med Biol. 2013;12(4):133-149. doi: 10.1007/s12522-013-0155-z. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Reprod Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 24273450 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the mystery associated with infertility and prostate cancer: an update.Med Oncol. 2023 Apr 26;40(6):160. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02028-3. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37099242 Review.
-
Environmental pollutants: genetic damage and epigenetic changes in male germ cells.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Dec;23(23):23339-23348. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7728-4. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27672044 Review.
-
Methylation analysis of histone H4K12ac-associated promoters in sperm of healthy donors and subfertile patients.Clin Epigenetics. 2015 Mar 19;7(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13148-015-0058-4. eCollection 2015. Clin Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25806092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ylij JMG, Schmidz W, Morton E. Zinc-induced Protamines ” Secondary Structure Transitions in Human Sperm. Peptides. 1990;265:20667–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
