The small GTPase RhoA regulates the contraction of smooth muscle tissues by catalyzing the assembly of cytoskeletal signaling complexes at membrane adhesion sites
- PMID: 22893699
- PMCID: PMC3464510
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.369603
The small GTPase RhoA regulates the contraction of smooth muscle tissues by catalyzing the assembly of cytoskeletal signaling complexes at membrane adhesion sites
Abstract
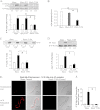
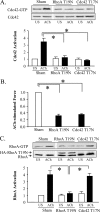
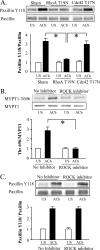
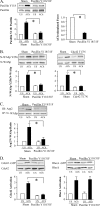
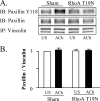
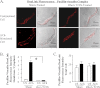
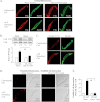
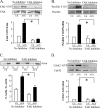
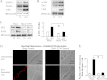
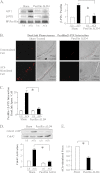
The activation of the small GTPase RhoA is necessary for ACh-induced actin polymerization and airway smooth muscle (ASM) contraction, but the mechanism by which it regulates these events is unknown. Actin polymerization in ASM is catalyzed by the actin filament nucleation activator, N-WASp and the polymerization catalyst, Arp2/3 complex. Activation of the small GTPase cdc42, a specific N-WASp activator, is also required for actin polymerization and tension generation. We assessed the mechanism by which RhoA regulates actin dynamics and smooth muscle contraction by expressing the dominant negative mutants RhoA T19N and cdc42 T17N, and non-phosphorylatable paxillin Y118/31F and paxillin ΔLD4 deletion mutants in SM tissues. Their effects were evaluated in muscle tissue extracts and freshly dissociated SM cells. Protein interactions and cellular localization were analyzed using proximity ligation assays (PLA), immunofluorescence, and GTPase and kinase assays. RhoA inhibition prevented ACh-induced cdc42 activation, N-WASp activation and the interaction of N-WASp with the Arp2/3 complex at the cell membrane. ACh induced paxillin phosphorylation and its association with the cdc42 GEFS, DOCK180 and α/βPIX. Paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation and its association with βPIX were RhoA-dependent, and were required for cdc42 activation. The ACh-induced recruitment of paxillin and FAK to the cell membrane was dependent on RhoA. We conclude that RhoA regulates the contraction of ASM by catalyzing the assembly and activation of cytoskeletal signaling modules at membrane adhesomes that initiate signaling cascades that regulate actin polymerization and tension development in response to contractile agonist stimulation. Our results suggest that the RhoA-mediated assembly of adhesome complexes is a fundamental step in the signal transduction process in response to agonist -induced smooth muscle contraction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel role for RhoA GTPase in the regulation of airway smooth muscle contraction.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Feb;93(2):129-36. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0388. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25531582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p21-Activated kinase (Pak) regulates airway smooth muscle contraction by regulating paxillin complexes that mediate actin polymerization.J Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;594(17):4879-900. doi: 10.1113/JP272132. Epub 2016 May 29. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27038336 Free PMC article.
-
Rho kinase collaborates with p21-activated kinase to regulate actin polymerization and contraction in airway smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2018 Aug;596(16):3617-3635. doi: 10.1113/JP275751. Epub 2018 Jun 24. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29746010 Free PMC article.
-
The adapter protein CrkII regulates neuronal Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, actin polymerization, and tension development during contractile stimulation of smooth muscle.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 17;280(24):23380-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413390200. Epub 2005 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15834156
-
Actin cytoskeletal dynamics in smooth muscle: a new paradigm for the regulation of smooth muscle contraction.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):C576-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00253.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18596210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of miR-185-5p as modulator of periostin synthesis and smooth muscle contraction in asthma.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Feb;237(2):1498-1508. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30620. Epub 2021 Oct 26. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34698372 Free PMC article.
-
RGS5 promotes arterial growth during arteriogenesis.EMBO Mol Med. 2014 Aug;6(8):1075-89. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201403864. EMBO Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24972930 Free PMC article.
-
Non-muscle (NM) myosin heavy chain phosphorylation regulates the formation of NM myosin filaments, adhesome assembly and smooth muscle contraction.J Physiol. 2017 Jul 1;595(13):4279-4300. doi: 10.1113/JP273906. Epub 2017 May 8. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28303576 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role for RhoA GTPase in the regulation of airway smooth muscle contraction.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Feb;93(2):129-36. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0388. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25531582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus Protease Alkaline Protease 1 (Alp1): A New Therapeutic Target for Fungal Asthma.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Jun 16;6(2):88. doi: 10.3390/jof6020088. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32560087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen W. E., Jones G. E., Pollard J. W., Ridley A. J. (1997) Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 regulate actin organization and cell adhesion in macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 110, 707–720 - PubMed
-
- Burridge K., Wennerberg K. (2004) Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell 116, 167–179 - PubMed
-
- DeMali K. A., Wennerberg K., Burridge K. (2003) Integrin signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 572–582 - PubMed
-
- Ridley A. J. (1999) Rho family proteins and regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Prog. Mol. Subcellul. Biol. 22, 1–22 - PubMed
-
- Ridley A. J. (2006) Rho GTPases and actin dynamics in membrane protrusions and vesicle trafficking. Trends Cell Biol. 16, 522–529 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

