Toward personalized hemodialysis by low molecular weight amino-containing compounds: future perspective of patient metabolic fingerprint
- PMID: 22890273
- PMCID: PMC3418613
- DOI: 10.2450/2012.012S
Toward personalized hemodialysis by low molecular weight amino-containing compounds: future perspective of patient metabolic fingerprint
Abstract
Background: L-carnitine deficiency is commonly observed in chronic hemodialysis patients, and this depletion may cause clinical symptoms like muscle weakness, anaemia, and hypotension.
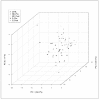
Materials and methods: We pursued a targeted metabonomics investigation in 28 hemodialysis patients (13 non diabetics and 15 diabetics) and in 10 age-matched healthy controls, on plasma levels of all carnitine esters and of several amino acids. Samples were taken before and after the first hemodialysis treatment of the week. Multiplexed data were collected in LCMRM (Multiple Reaction Monitoring) and analysed by unsupervised multivariate analysis.
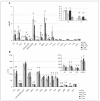
Results: In diabetic uremic patients, we observed lower values of propionylcarnitine than in other groups, while acylcarnitine concentration was higher in uremics compared to controls. The hemodialysis session induced a decline in free, short-chain, medium-chain and dicarboxylic acylcarnitines, whereas the long chain acylcarnitines remained unaffected. Plasma levels of amino acid proline, ornithine, citrulline and serine were significantly elevated in uremic patients before dialysis compared to controls. For most tested plasma amino acids, a significant reduction after hemodialysis session was found.
Discussion: Our study is the first that investigated on possible modifications of the system of carnitine in diabetic patients in hemodialysis not only in relation to the condition of deficiency but also compared to lipid and glucose homeostasis alteration typical of diabetics. We proposed the application of targeted metabolic fingerprint in the management of the hemodialysis patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of hemodialysis session on the dynamics of carnitine ester profile changes in L-carnitine pretreated end-stage renal disease patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2013 Jun;45(3):847-55. doi: 10.1007/s11255-012-0209-x. Epub 2012 Jun 10. Int Urol Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 22684763
-
Impact of hemodialysis on endogenous plasma and muscle carnitine levels in patients with end-stage renal disease.Kidney Int. 2004 Oct;66(4):1527-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00916.x. Kidney Int. 2004. PMID: 15458447
-
Carnitine depletion as a probable cause of hyperlipidemia in uremic patients on maintenance hemodialysis.Tohoku J Exp Med. 1983 Jan;139(1):33-42. doi: 10.1620/tjem.139.33. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1983. PMID: 6836557
-
Carnitine and hemodialysis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2003 Mar;41(3 Suppl 1):S116-22. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2003.50099. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003. PMID: 12612967 Review.
-
1alpha(OH)D3 One-alpha-hydroxy-cholecalciferol--an active vitamin D analog. Clinical studies on prophylaxis and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in uremic patients on chronic dialysis.Dan Med Bull. 2008 Nov;55(4):186-210. Dan Med Bull. 2008. PMID: 19232159 Review.
Cited by
-
Tear Film Steroid Profiling in Dry Eye Disease by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 24;18(7):1349. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071349. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28672794 Free PMC article.
-
Change in Anemia by Carnitine Supplementation in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Retrospective Observational Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 5;8:767945. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.767945. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34805230 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Lipidomics and Metabolomics Analysis of Tears in Multiple Sclerosis: An Insight into Diagnostic Potential of Lacrimal Fluid.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 13;20(6):1265. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061265. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30871169 Free PMC article.
-
L-Carnitine status in end-stage renal disease patients on automated peritoneal dialysis.J Nephrol. 2014 Dec;27(6):699-706. doi: 10.1007/s40620-014-0076-x. Epub 2014 Mar 6. J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24599831
-
Breast cancer stem cells rely on fermentative glycolysis and are sensitive to 2-deoxyglucose treatment.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jul 17;5(7):e1336. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.285. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25032859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evans A. Dialysis-related carnitine disorder and levocarnitine pharmacology. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:S13–26. - PubMed
-
- Guarnieri G, Situlin R, Biolo G. Carnitine metabolism in uremia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38(Suppl 1):S63–7. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S. L-carnitine in dialysis patients. Semin Dial. 2001;14:209–17. - PubMed
-
- Hoppel C. The role of carnitine in normal and altered fatty acid metabolism. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:S4–12. - PubMed
-
- Evans AM, Faull R, Fornasini G, et al. Pharmacokinetics of L-carnitine in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing long-term hemodialysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000;68:238–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
