Recombinant high-density lipoprotein nanoparticles containing gadolinium-labeled cholesterol for morphologic and functional magnetic resonance imaging of the liver
- PMID: 22888232
- PMCID: PMC3414207
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S33139
Recombinant high-density lipoprotein nanoparticles containing gadolinium-labeled cholesterol for morphologic and functional magnetic resonance imaging of the liver
Abstract
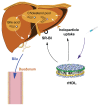
Background: Natural high-density lipoproteins (HDL) possess important physiological functions to the transport of cholesterol from the peripheral tissues to the liver for metabolic degradation and excretion in the bile.
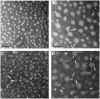
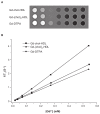
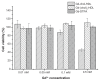
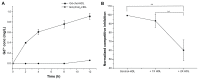
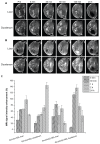
Methods and results: In this work, we took advantage of this pathway and prepared two different gadolinium (Gd)-DTPA-labeled cholesterol-containing recombinant HDL nanoparticles (Gd-chol-HDL) and Gd-(chol)(2)-HDL as liver-specific magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. The reconstituted HDL nanoparticles had structural similarity to native HDL, and could be taken up by HepG2 cells via interaction with HDL receptors in vitro. In vivo MRI studies in rats after intravenous injections of 10 μmol gadolinium per kg of recombinant HDL nanoparticles indicated that both nanoparticles could provide signal enhancement in the liver and related organs. However, different T(1)-weighted image details suggested that they participated in different cholesterol metabolism and excretion pathways in the liver.
Conclusion: Such information could be highly useful to differentiate functional changes as well as anatomic differences in the liver. These cholesterol-derived contrast agents and their recombinant HDL preparations may warrant further development as a new class of contrast agents for MRI of the liver and related organs.
Keywords: apolipoprotein; contrast agent; gadolinium; high-density lipoprotein; liver; magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gadolinium-conjugated PLA-PEG nanoparticles as liver targeted molecular MRI contrast agent.J Drug Target. 2011 Sep;19(8):657-65. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2010.531727. Epub 2010 Nov 23. J Drug Target. 2011. PMID: 21091273
-
Recombinant HDL-like nanoparticles: a specific contrast agent for MRI of atherosclerotic plaques.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Dec 22;126(50):16316-7. doi: 10.1021/ja044911a. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15600321
-
Comparison of synthetic high density lipoprotein (HDL) contrast agents for MR imaging of atherosclerosis.Bioconjug Chem. 2009 May 20;20(5):937-43. doi: 10.1021/bc800520d. Bioconjug Chem. 2009. PMID: 19378935 Free PMC article.
-
High-Density Lipoproteins: Nature's Multifunctional Nanoparticles.ACS Nano. 2016 Mar 22;10(3):3015-41. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b07522. Epub 2016 Feb 25. ACS Nano. 2016. PMID: 26889958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-based systems for T(1)-weighted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 21;14(5):10591-607. doi: 10.3390/ijms140510591. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23698781 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nature-inspired nanoformulations for contrast-enhanced in vivo MR imaging of macrophages.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2014 Sep-Oct;9(5):372-82. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.1587. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24729189 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Delivery Strategies for Antivirals against Hepatitis B Virus.Viruses. 2018 May 17;10(5):267. doi: 10.3390/v10050267. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29772748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Gadolinium Based Contrast Agents for Bioimaging Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Sep 20;11(9):2449. doi: 10.3390/nano11092449. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34578765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Labeling, Visualization, and Quantification of Hyaluronan Distribution in Tumor-Bearing Mouse Using PET and MR Imaging.Pharm Res. 2020 Nov 4;37(12):237. doi: 10.1007/s11095-020-02957-y. Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 33151373
-
Understanding the Exchange of Systemic HDL Particles Into the Brain and Vascular Cells Has Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 6;12:700847. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.700847. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34552500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caravan P, Ellison JJ, McMurry TJ, Lauffer RB. Gadolinium (III) chelates as MRI contrast agents: structure, dynamics, and applications. Chem Rev. 1999;99(9):2293–2352. - PubMed
-
- Geraldes CF, Laurent S. Classification and basic properties of contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2009;4(1):1–23. - PubMed
-
- Seale MK, Catalano OA, Saini S, Hahn PF, Sahani DV. Hepatobiliary-specific MR contrast agents: role in imaging the liver and biliary tree. Radiographics. 2009;29(6):1725–1748. - PubMed
-
- Langereis S, Dirksen A, Hackeng TM, van Genderen MHP, Meijer EW. Dendrimers and magnetic resonance imaging. New J Chem. 2007;31(7):1152–1160.
-
- Luo K, Liu G, He B, et al. Multifunctional gadolinium-based dendritic macromolecules as liver targeting imaging probes. Biomaterials. 2011;32(10):2575–2585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

