Metabolic activation of the HOG MAP kinase pathway by Snf1/AMPK regulates lipid signaling at the Golgi
- PMID: 22882253
- PMCID: PMC3465495
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2012.01406.x
Metabolic activation of the HOG MAP kinase pathway by Snf1/AMPK regulates lipid signaling at the Golgi
Abstract
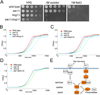
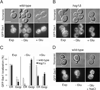
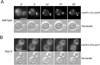
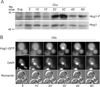
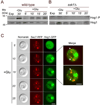
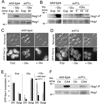
Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI(4)P) is an important regulator of Golgi function. Metabolic regulation of Golgi PI(4)P requires the lipid phosphatase Sac1 that translocates between endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi membranes. Localization of Sac1 responds to changes in glucose levels, yet the upstream signaling pathways that regulate Sac1 traffic are unknown. Here, we report that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) Hog1 transmits glucose signals to the Golgi and regulates localization of Sac1. We find that Hog1 is rapidly activated by both glucose starvation and glucose stimulation, which is independent of the well-characterized response to osmotic stress but requires the upstream element Ssk1 and is controlled by Snf1, the yeast homolog of AMP-activated kinase (AMPK). Elimination of either Hog1 or Snf1 slows glucose-induced translocation of Sac1 lipid phosphatase from the Golgi to the ER and thus delays PI(4)P accumulation at the Golgi. We conclude that a novel cross-talk between the HOG pathway and Snf1/AMPK is required for the metabolic control of lipid signaling at the Golgi.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae AMPK, Snf1, Negatively Regulates the Hog1 MAPK Pathway in ER Stress Response.PLoS Genet. 2015 Sep 22;11(9):e1005491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005491. eCollection 2015. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26394309 Free PMC article.
-
Accumulation of PtdIns(4)P at the Golgi mediated by reversible oxidation of the PtdIns(4)P phosphatase Sac1 by H2O2.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Jan;130:426-435. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30448513
-
Oxysterol-binding protein recruitment and activity at the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi interface are independent of Sac1.Traffic. 2017 Aug;18(8):519-529. doi: 10.1111/tra.12491. Epub 2017 May 31. Traffic. 2017. PMID: 28471037
-
Growth and metabolic control of lipid signalling at the Golgi.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Feb;40(1):205-9. doi: 10.1042/BST20110637. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22260691 Review.
-
SNF1/AMPK pathways in yeast.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2408-20. doi: 10.2741/2854. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transient activation of fission yeast AMPK is required for cell proliferation during osmotic stress.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jul 1;28(13):1804-1814. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-04-0235. Epub 2017 May 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28515144 Free PMC article.
-
Host Lung Environment Limits Aspergillus fumigatus Germination through an SskA-Dependent Signaling Response.mSphere. 2021 Dec 22;6(6):e0092221. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00922-21. Epub 2021 Dec 8. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34878292 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of glucose-dependent gene expression by the RNA helicase Dbp2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2014 Nov;198(3):1001-14. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.170019. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25164881 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed Turnover of Unphosphorylated Ssk1 during Carbon Stress Activates the Yeast Hog1 Map Kinase Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 4;10(9):e0137199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137199. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26340004 Free PMC article.
-
Directed Evolution Reveals Unexpected Epistatic Interactions That Alter Metabolic Regulation and Enable Anaerobic Xylose Use by Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 14;12(10):e1006372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006372. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27741250 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

