Rescue of internalization-defective platelet-activating factor receptor function by EBP50/NHERF1
- PMID: 22878922
- PMCID: PMC3497898
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-012-0175-1
Rescue of internalization-defective platelet-activating factor receptor function by EBP50/NHERF1
Abstract
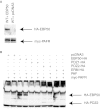
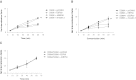
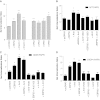
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a potent phospholipid mediator involved in specific disease states such as allergic asthma, atherosclerosis and psoriasis. The human PAF receptor (PAFR) is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Following PAF stimulation, cells become rapidly desensitized; this refractory state can be maintained for hours and is dependent on PAFR phosphorylation, internalization and trafficking. EBP50/NHERF1 has been found to interact with a variety of proteins and these interactions are involved in a growing range of functions including the assembly of signalling complexes, receptor recycling and transport of proteins to the cell surface. Crucial roles of EBP50 in GPCR physiology include its involvement in internalization, recycling, and downregulation. We were interested in identifying the role of EBP50 in PAFR trafficking. Our results showed that EBP50 binds the PAFR in its basal state, while stimulation decreased the ratio of interaction between the two proteins. We also demonstrated that EBP50 could bind PAFR via its PDZ 2 domain. In addition, we studied the role of EBP50 in various functions of the PAFR such as PAF-induced inositol phosphate accumulation and receptor internalization: EBP50 decreased the WT PAFR response and rescued the function of internalization-deficient mutant receptors, as previously described for the arrestins and the GRKs. These results suggest new roles for EBP50, some of which could help understanding the complex formation after receptor activation.
Figures


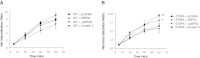
Similar articles
-
Trafficking, ubiquitination, and down-regulation of the human platelet-activating factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 28;278(48):48228-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304082200. Epub 2003 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 14500726
-
Inverse agonist-induced signaling and down-regulation of the platelet-activating factor receptor.Cell Signal. 2007 Oct;19(10):2068-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.05.015. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17609120
-
Agonist-induced internalization of the platelet-activating factor receptor is dependent on arrestins but independent of G-protein activation. Role of the C terminus and the (D/N)PXXY motif.J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 1;277(9):7356-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110058200. Epub 2001 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11729201
-
Signalling or binding: the role of the platelet-activating factor receptor in invasive pneumococcal disease.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Jun;15(6):870-81. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12129. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23444839 Review.
-
Roles of NHERF1/EBP50 in cancer.Curr Mol Med. 2008 Sep;8(6):459-68. doi: 10.2174/156652408785748031. Curr Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18781953 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of platelet-activating factor-mediated interleukin-6 promoter activation by the 48 kDa but not the 45 kDa isoform of protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2.Cell Biosci. 2019 Jun 25;9:51. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0316-9. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31289638 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA-Rho kinase and platelet-activating factor stimulation of ovine foetal pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.Cell Prolif. 2013 Oct;46(5):563-75. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12052. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Cell Prolif. 2013. PMID: 24033386 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism by which nuclear factor-kappa beta (NF-kB) regulates ovine fetal pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2015 Jun 3;4:11-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2015.05.003. eCollection 2015 Sep. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2015. PMID: 26966681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brocheriou I, Stengel D, Mattsson-Hulten L, Stankova J, Rola-Pleszczynski M, Koskas F, Wiklund O, Charpentier Y, Ninio E. Expression of platelet-activating factor receptor in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques: relevance to progression of atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2000;102(21):2569–2575. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.21.2569. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Dupre DJ, Gouill C, Rola-Pleszczynski M, Stankova J. Agonist-induced internalization of the platelet-activating factor receptor is dependent on arrestins but independent of G-protein activation. Role of the C terminus and the (D/N)PXXY motif. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(9):7356–7362. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110058200. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

