Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2
- PMID: 22869320
- PMCID: PMC4011499
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-012-2644-8
Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2
Abstract
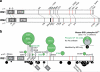
The insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2 are key targets of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase and are required for hormonal control of metabolism. Tissues from insulin-resistant and diabetic humans exhibit defects in IRS-dependent signalling, implicating their dysregulation in the initiation and progression of metabolic disease. However, IRS1 and IRS2 are regulated through a complex mechanism involving phosphorylation of >50 serine/threonine residues (S/T) within their long, unstructured tail regions. In cultured cells, insulin-stimulated kinases (including atypical PKC, AKT, SIK2, mTOR, S6K1, ERK1/2 and ROCK1) mediate feedback (autologous) S/T phosphorylation of IRS, with both positive and negative effects on insulin sensitivity. Additionally, insulin-independent (heterologous) kinases can phosphorylate IRS1/2 under basal conditions (AMPK, GSK3) or in response to sympathetic activation and lipid/inflammatory mediators, which are present at elevated levels in metabolic disease (GRK2, novel and conventional PKCs, JNK, IKKβ, mPLK). An emerging view is that the positive/negative regulation of IRS by autologous pathways is subverted/co-opted in disease by increased basal and other temporally inappropriate S/T phosphorylation. Compensatory hyperinsulinaemia may contribute strongly to this dysregulation. Here, we examine the links between altered patterns of IRS S/T phosphorylation and the emergence of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Figures
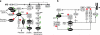

Similar articles
-
Insulin and metabolic stress stimulate multisite serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 and inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 2;289(18):12467-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554162. Epub 2014 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24652289 Free PMC article.
-
Salicylic acid reverses phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)- and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha)-induced insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) serine 307 phosphorylation and insulin resistance in human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 3;278(1):180-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205565200. Epub 2002 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12409308
-
Resistin promotes cardiac hypertrophy via the AMP-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin (AMPK/mTOR) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase/insulin receptor substrate 1 (JNK/IRS1) pathways.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 27;286(21):18465-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.200022. Epub 2011 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21478152 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance: role of stress-regulated serine kinases and insulin receptor substrates (IRS) serine phosphorylation.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;9(6):753-62. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.07.004. Epub 2009 Aug 13. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19683471 Review.
-
Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling through IRS-1 phosphorylation.Biochimie. 2005 Jan;87(1):99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.10.019. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 15733744 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin signaling in type 2 diabetes: experimental and modeling analyses reveal mechanisms of insulin resistance in human adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 5;288(14):9867-9880. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432062. Epub 2013 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23400783 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo biloba Extract 50 (GBE50) Ameliorates Insulin Resistance, Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice.J Inflamm Res. 2021 May 17;14:1959-1971. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S302934. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34040411 Free PMC article.
-
The Insulin Receptor Adaptor IRS2 is an APC/C Substrate That Promotes Cell Cycle Protein Expression and a Robust Spindle Assembly Checkpoint.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Sep;19(9):1450-1467. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.002069. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32554797 Free PMC article.
-
Glucosamine and Its Analogues as Modulators of Amyloid-β Toxicity.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021 Mar 24;12(4):548-554. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00350. eCollection 2021 Apr 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 33859794 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the pSer/pThr dependent regulation of the SHP2 tyrosine phosphatase in insulin and CD28 signaling.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 16;13(1):5439. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32918-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36114179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reaven G. The metabolic syndrome or the insulin resistance syndrome? Different names, different concepts, and different goals. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004;33:283–303. - PubMed
-
- Biddinger SB, Kahn CR. From mice to men: insights into the insulin resistance syndromes. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:123–158. - PubMed
-
- Karlsson HK, Zierath JR. Insulin signaling and glucose transport in insulin resistant human skeletal muscle. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2007;48:103–113. - PubMed
-
- Boura-Halfon S, Zick Y. Phosphorylation of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;296:E581–E591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

