Factors associated with local-regional recurrence after a negative sentinel node dissection: results of the ACOSOG Z0010 trial
- PMID: 22868365
- PMCID: PMC5345746
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182654494
Factors associated with local-regional recurrence after a negative sentinel node dissection: results of the ACOSOG Z0010 trial
Abstract
Objective: To determine factors important in local-regional recurrence (LRR) in patients with negative sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining.
Background: Z0010 was a prospective multicenter trial initiated in 1999 by the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group to evaluate occult disease in SLNs and bone marrow of early-stage breast cancer patients. Participants included women with biopsy-proven T1-2 breast cancer with clinically negative nodes, planned for lumpectomy and whole breast irradiation.
Methods: Women with clinical T1-2,N0,M0 disease underwent lumpectomy and SLN dissection. There was no axillary-specific treatment for H&E-negative SLNs, and clinicians were blinded to immunohistochemistry results. Systemic therapy was based on primary tumor factors. Univariable and multivariable analyses were performed to determine clinicopathologic factors associated with LRR.
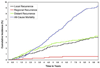
Results: Of 5119 patients, 3904 (76.3%) had H&E-negative SLNs. Median age was 57 years (range 23-95). At median follow-up of 8.4 years, there were 127 local, 20 regional, and 134 distant recurrences. Factors associated with local-regional recurrence were hormone receptor-negative disease (P = 0.0004) and younger age (P = 0.047). In competing risk-regression models, hormone receptor-positive disease and use of chemotherapy were associated with reduction in local-regional recurrence. When local recurrence was included in the model as a time-dependent variable, older age, T2 disease, high tumor grade, and local recurrence were associated with reduced overall survival.
Conclusions: Local-regional recurrences are rare in early-stage breast cancer patients with H&E-negative SLNs. Younger age and hormone receptor-negative disease are associated with higher event rates, and local recurrence is associated with reduced overall survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eight-year follow up result of the OTOASOR trial: The Optimal Treatment Of the Axilla - Surgery Or Radiotherapy after positive sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer: A randomized, single centre, phase III, non-inferiority trial.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017 Apr;43(4):672-679. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28139362 Clinical Trial.
-
Are there patients with T1 to T2, lymph node-negative breast cancer who are "high-risk" for locoregional disease recurrence?Cancer. 2017 Jul 15;123(14):2626-2633. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30658. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28334423 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Axillary Dissection vs No Axillary Dissection on 10-Year Overall Survival Among Women With Invasive Breast Cancer and Sentinel Node Metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2017 Sep 12;318(10):918-926. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28898379 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Update on the NSABP and ACOSOG breast cancer sentinel node trials.Am Surg. 2004 May;70(5):420-4. Am Surg. 2004. PMID: 15156950 Review.
-
259 Patients with DCIS of the breast applying USC/Van Nuys prognostic index: a retrospective review with long term follow up.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008 Jun;109(3):405-16. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9668-7. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. PMID: 17687650 Review.
Cited by
-
Positive Axilla in Breast Cancer; Clinical Practice in 2018.Eur J Breast Health. 2018 Jul 1;14(3):134-135. doi: 10.5152/ejbh.2018.4132. eCollection 2018 Jul. Eur J Breast Health. 2018. PMID: 30123877 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diverse Distribution and Gene Expression on the 21-Gene Recurrence Assay in Breast Cancer Patients with Locoregional Recurrence Versus Distant Metastasis.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Aug 10;13:6279-6289. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S314461. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34408490 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy in clinically node-positive breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 11;9(9):e105316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105316. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25210779 Free PMC article.
-
Conserving the axilla in breast cancer.Ecancermedicalscience. 2020 Aug 18;14:1090. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2020.1090. eCollection 2020. Ecancermedicalscience. 2020. PMID: 33014132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can a subgroup at high risk for LRR be identified from T1-2 breast cancer with negative lymph nodes after mastectomy? A meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2019 Sep 20;39(9):BSR20181853. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181853. Print 2019 Sep 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31484798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, et al. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: the ALMANAC trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, et al. Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:881–888. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Viale G, Paganelli G, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: ten-year results of a randomized controlled study. Ann Surg. 2010;251:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Bergkvist L, de Boniface JP-EJ, et al. Axillary Recurrence Rate After Negative Sentinel Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer. Three-Year Follow-Up of the Swedish Multicenter Cohort Study. Ann Surg. 2008;247:150–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical