MicroRNA 21 inhibits left ventricular remodeling in the early phase of rat model with ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing cell apoptosis
- PMID: 22859901
- PMCID: PMC3410360
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.4514
MicroRNA 21 inhibits left ventricular remodeling in the early phase of rat model with ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing cell apoptosis
Abstract
Objective: To determine the role of microRNA 21(miR-21) on left ventricular remodeling of rat heart with ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury and to investigate the underlying mechanism of miR-21 mediated myocardium protection.
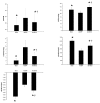
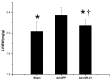
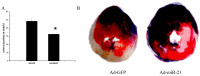
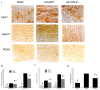
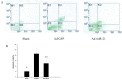
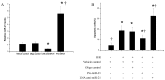
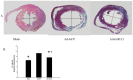
Methods: Rats were randomly divided into three groups: an I/R model group with Ad-GFP (Ad-GFP group), an I/R model group with Ad-miR-21 (Ad-miR-21 group) and a sham-surgery group. Changes in hemodynamic parameters were recorded at 1 week after I/R. Histological diagnosis was achieved by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Left ventricular (LV) dimensions, myocardial infarct size, LV/BW, collagen type Ⅰ, type Ⅲ and PCNA positive cells were measured. Primary cultures of neonatal rat cardiac ventricular myocytes were performed and cell ischemic injury was induced by hypoxia in a serum- and glucose-free medium, and reoxygenation (H/R). MiR-21 inhibitor and pre-miR-21 were respectively added to the culture medium for the miR-21 knockdown and for the miR-21 up-regulation. qRT-PCR was used to determine the miR-21 levels in cultured cells. Flow cytometry was performed to examine the cell apoptosis.
Results: In the Ad-miR-21 group, LV dimensions, myocardial infarct size, LV/BW, collagen type Ⅰ, type Ⅲ and PCNA positive cells all significantly decreased compared with the Ad-GFP group. At 1 week after I/R, the Ad-miR-21 significantly improved LVSP, LV +dp/dt(max), LV - dp/dt(min), and decreased heart rate (HR) and LVEDP compared with the Ad-GFP group. Compared with the Ad-GFP, the cell apoptotic rate significantly decreased in the Ad-miR-21 group. The miR-21 inhibitor exacerbated cardiac myocyte apoptosis and the pre-miR-21 decreased hypoxia/reoxygenation- induced cardiac myocyte apoptosis.
Conclusions: Ad-miR-21 improves LV remodeling and decreases the apoptosis of myocardial cells, suggesting the possible mechanism by which Ad-miR-21 functions in protecting against I/R injury.
Keywords: apoptosis; collagen; hemodynamic; ischemia-reperfusion; microRNA 21; rat.; ventricular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-214 Inhibits Left Ventricular Remodeling in an Acute Myocardial Infarction Rat Model by Suppressing Cellular Apoptosis via the Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN).Int Heart J. 2016;57(2):247-50. doi: 10.1536/ihj.15-293. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Int Heart J. 2016. PMID: 26973267
-
The protective effect of microRNA-320 on left ventricular remodeling after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat model.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 29;15(10):17442-56. doi: 10.3390/ijms151017442. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25268616 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Effect of MicroRNA-21 in Murine Myocardial Infarction.Cardiovasc Ther. 2015 Jun;33(3):109-17. doi: 10.1111/1755-5922.12118. Cardiovasc Ther. 2015. PMID: 25809568
-
LncRNA HIF1A-AS1 contributes to ventricular remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by adsorption of microRNA-204 to regulating SOCS2 expression.Cell Cycle. 2019 Oct;18(19):2465-2480. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1648960. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Cell Cycle. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2022 Apr;21(7):756. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.2014700. PMID: 31354024 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Role of microRNAs in the reperfused myocardium towards post-infarct remodelling.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 May 1;94(2):284-92. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr291. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22038740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 protects cardiomyocytes from oxygen-glucose deprivation injuries by targeting microRNA-21.Exp Ther Med. 2019 May;17(5):3709-3716. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7330. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30988756 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-7a/b protects against cardiac myocyte injury in ischemia/reperfusion by targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 3;9(3):e90096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090096. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24594984 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental verification of a conserved intronic microRNA located in the human TrkC gene with a cell type-dependent apoptotic function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jul;72(13):2613-25. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1868-4. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25772499 Free PMC article.
-
Current RNA strategies in treating cardiovascular diseases.Mol Ther. 2024 Mar 6;32(3):580-608. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.01.028. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38291757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An epicardial delivery of nitroglycerine by active hydraulic ventricular support drug delivery system improves cardiac function in a rat model.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020 Feb;10(1):23-33. doi: 10.1007/s13346-019-00656-9. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 31240626
References
-
- Fox CS, Coady S, Sorlie PD. et al. Increasing cardiovascular disease burden due to diabetes mellitus: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2007;115:1544–50. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Zhang JQ, Zhang J. et al. Cardiac remodeling by fibrous tissue after infarction in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 2000;135:316–23. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 2003;113:673–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

