Evolution of the vertebrate paralemmin gene family: ancient origin of gene duplicates suggests distinct functions
- PMID: 22855693
- PMCID: PMC3405040
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041850
Evolution of the vertebrate paralemmin gene family: ancient origin of gene duplicates suggests distinct functions
Abstract
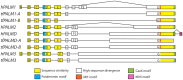
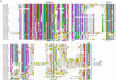
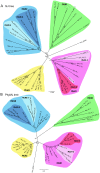
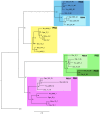
Paralemmin-1 is a protein implicated in plasma membrane dynamics, the development of filopodia, neurites and dendritic spines, as well as the invasiveness and metastatic potential of cancer cells. However, little is known about its mode of action, or about the biological functions of the other paralemmin isoforms: paralemmin-2, paralemmin-3 and palmdelphin. We describe here evolutionary analyses of the paralemmin gene family in a broad range of vertebrate species. Our results suggest that the four paralemmin isoform genes (PALM1, PALM2, PALM3 and PALMD) arose by quadruplication of an ancestral gene in the two early vertebrate genome duplications. Paralemmin-1 and palmdelphin were further duplicated in the teleost fish specific genome duplication. We identified a unique sequence motif common to all paralemmins, consisting of 11 highly conserved residues of which four are invariant. A single full-length paralemmin homolog with this motif was identified in the genome of the sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus and an isolated putative paralemmin motif could be detected in the genome of the lancelet Branchiostoma floridae. This allows us to conclude that the paralemmin gene family arose early and has been maintained throughout vertebrate evolution, suggesting functional diversification and specific biological roles of the paralemmin isoforms. The paralemmin genes have also maintained specific features of gene organisation and sequence. This includes the occurrence of closely linked downstream genes, initially identified as a readthrough fusion protein with mammalian paralemmin-2 (Palm2-AKAP2). We have found evidence for such an arrangement for paralemmin-1 and -2 in several vertebrate genomes, as well as for palmdelphin and paralemmin-3 in teleost fish genomes, and suggest the name paralemmin downstream genes (PDG) for this new gene family. Thus, our findings point to ancient roles for paralemmins and distinct biological functions of the gene duplicates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The paralemmin protein family: identification of paralemmin-2, an isoform differentially spliced to AKAP2/AKAP-KL, and of palmdelphin, a more distant cytosolic relative.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Aug 3;285(5):1369-76. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5329. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11478809
-
Paralemmin, a prenyl-palmitoyl-anchored phosphoprotein abundant in neurons and implicated in plasma membrane dynamics and cell process formation.J Cell Biol. 1998 Nov 2;143(3):795-813. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.3.795. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9813098 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization and immunohistochemical localization of palmdelphin, a cytosolic isoform of the paralemmin protein family implicated in membrane dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;84(11):853-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2005.07.002. Eur J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16323283
-
Evolutionary genetics of vertebrate tissue mineralization: the origin and evolution of the secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein family.J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2006 May 15;306(3):295-316. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.21088. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2006. PMID: 16358265 Review.
-
Impact of gene gains, losses and duplication modes on the origin and diversification of vertebrates.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 Feb;24(2):83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.12.008. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23291262 Review.
Cited by
-
Palmdelphin Regulates Nuclear Resilience to Mechanical Stress in the Endothelium.Circulation. 2021 Nov 16;144(20):1629-1645. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.054182. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 34636652 Free PMC article.
-
The vertebrate ancestral repertoire of visual opsins, transducin alpha subunits and oxytocin/vasopressin receptors was established by duplication of their shared genomic region in the two rounds of early vertebrate genome duplications.BMC Evol Biol. 2013 Nov 2;13:238. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-13-238. BMC Evol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24180662 Free PMC article.
-
In-depth proteomic analysis of mouse cochlear sensory epithelium by mass spectrometry.J Proteome Res. 2013 Aug 2;12(8):3620-30. doi: 10.1021/pr4001338. Epub 2013 Jun 26. J Proteome Res. 2013. PMID: 23721421 Free PMC article.
-
Different responses to risperidone treatment in Schizophrenia: a multicenter genome-wide association and whole exome sequencing joint study.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Apr 28;12(1):173. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01942-w. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35484098 Free PMC article.
-
Heritability and genetic association analysis of cognition in the Diabetes Heart Study.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Aug;35(8):1958.e3-1958.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.03.005. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24684796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu B, Petrasch-Parwez E, Laue M, Kilimann M. Molecular characterization and immunohistochemical localization of palmdelphin, a cytosolic isoform of the paralemmin protein family implicated in membrane dynamics. Eur J Cell Biol. 2005;84:853–866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

