Chronic Inflammation and Coronary Atherosclerosis in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
- PMID: 22851960
- PMCID: PMC3376340
- DOI: 10.1159/000337082
Chronic Inflammation and Coronary Atherosclerosis in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
Abstract
The key role of chronic inflammation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis has become increasingly apparent in recent years based on the results of experimental, epidemiologic and clinical studies. Coronary artery disease and its complications occur with disproportionately high frequency in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and contribute substantially to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in this population. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors occur commonly in patients with ESRD. In addition, a variety of patient-related and dialysis-related factors unique to ESRD predispose to chronic inflammation and by doing so are thought to contribute to coronary atherosclerosis and its complications. These risk factors may serve as therapeutic targets and as such may offer the potential for altering the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis in ESRD.
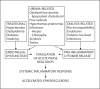
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peri-aortic fat tissue and malnutrition-inflammation-atherosclerosis/calcification syndrome in end-stage renal disease patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2013 Jun;45(3):857-67. doi: 10.1007/s11255-012-0286-x. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Int Urol Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23001639
-
Traditional and non-traditional risk factors as contributors to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in end-stage renal disease.Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2004;38(5):405-16. doi: 10.1080/00365590410031715. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 15764253 Review.
-
Screening and risk stratification of coronary artery disease in end-stage renal disease.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014 Jul;7(7):715-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.12.015. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014. PMID: 25034921 Review.
-
Predictive markers of asymptomatic atherosclerosis in end-stage renal disease patients.Ren Fail. 2010 May;32(4):448-54. doi: 10.3109/08860221003658258. Ren Fail. 2010. PMID: 20446782
-
Systemic inflammation in dialysis patients with end-stage renal disease: causes and consequences.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2004 Sep;56(3):237-48. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2004. PMID: 15467502 Review.
Cited by
-
The neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis in peritoneal dialysis patients.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2294149. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2294149. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38178381 Free PMC article.
-
Intradialytic hypotension is an important risk factor for critical limb ischemia in patients on hemodialysis.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Dec 19;20(1):473. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1662-x. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31856757 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review on apolipoproteins as nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors in end-stage renal disease: current evidence and perspectives.Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Jul;51(7):1173-1189. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02170-w. Epub 2019 May 22. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31119518 Review.
-
C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in hemodialysis patients.Caspian J Intern Med. 2013 Winter;4(1):611-6. Caspian J Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 24009946 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating hepassocin level in patients with stable angina is associated with fatty liver and renal function.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(1):1-7. doi: 10.7150/ijms.50646. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leitinger N. Oxidized phospholipids as modulators of inflammation in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2003;14:421–430. - PubMed
-
- Dai G, Kaazempur-Mofrad MR, Natarajan S, Zhang Y, Vaughn S, Blackman BR, Kamm RD, Garcia-Cardena G, Gimbrone MA., Jr Distinct endothelial phenotypes evoked by arterial waveforms derived from atherosclerosis-susceptible and resistant regions of human vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:14871–14876. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cybulsky MI, Gimbrone MA., Jr Endothelial expression of a mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecule during atherogenesis. Science. 1991;251:788–791. - PubMed
-
- Boring L, Gosling J, Cleary M, Charo IF. Decreased lesion formation in CCR2-/- mice reveals a role for chemokines in the initiation of atherosclerosis. Nature. 1998;394:894–897. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
