Elevated IKKα accelerates the differentiation of human neuronal progenitor cells and induces MeCP2-dependent BDNF expression
- PMID: 22848609
- PMCID: PMC3407048
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041794
Elevated IKKα accelerates the differentiation of human neuronal progenitor cells and induces MeCP2-dependent BDNF expression
Abstract
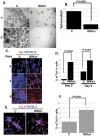
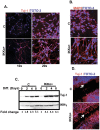
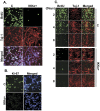
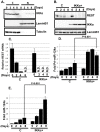
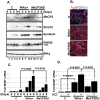
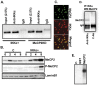
The IκB kinase α (IKKα) is implicated in the differentiation of epithelial and immune cells. We examined whether IKKα also plays a role in the differentiation and maturation of embryonic human neuronal progenitor cells (NPCs). We find that expression of an extra copy of IKKα (IKKα+) blocks self-renewal and accelerates the differentiation of NPCs. This coincides with reduced expression of the Repressor Element Silencing Transcription Factor/Neuron-Restrictive Silencing Factor (REST/NRSF), which is a prominent inhibitor of neurogenesis, and subsequent induction of the pro-differentiation non-coding RNA, miR-124a. However, the effects of IKKα on REST/NRSF and miR-124a expression are likely to be indirect. IKKα+ neurons display extensive neurite outgrowth and accumulate protein markers of neuronal maturation such as SCG10/stathmin-2, postsynaptic density 95 (PSD95), syntaxin, and methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2). Interestingly, IKKα associates with MeCP2 in the nuclei of human neurons and can phosphorylate MeCP2 in vitro. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we find that IKKα is recruited to the exon-IV brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promoter, which is a well-characterized target of MeCP2 activity. Moreover, IKKα induces the transcription of BDNF and knockdown expression of MeCP2 interferes with this event. These studies highlight a role for IKKα in accelerating the differentiation of human NPCs and identify IKKα as a potential regulator of MeCP2 function and BDNF expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of miR-15a Promotes BDNF Expression and Rescues Dendritic Maturation Deficits in MeCP2-Deficient Neurons.Stem Cells. 2015 May;33(5):1618-29. doi: 10.1002/stem.1950. Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25639236 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-197 controls ADAM10 expression to mediate MeCP2's role in the differentiation of neuronal progenitors.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Oct;26(10):1863-1879. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0257-6. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30560934 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-22 regulates smooth muscle cell differentiation from stem cells by targeting methyl CpG-binding protein 2.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Apr;35(4):918-29. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.305212. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25722434
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) by Methyl CpG Binding Protein 2 (MeCP2): a Novel Mechanism for Re-Myelination and/or Myelin Repair Involved in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Mar;53(2):1092-1107. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9074-1. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25579386 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain REST/NRSF Is Not Only a Silent Repressor but Also an Active Protector.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):541-550. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9658-4. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26742529 Review.
-
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into corneal epithelial progenitor cells under defined conditions.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 15;12(8):e0183303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183303. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28813511 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of axon outgrowth and regeneration in CNS injury: the first steps forward.Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Oct;10(4):771-81. doi: 10.1007/s13311-013-0203-8. Neurotherapeutics. 2013. PMID: 23881454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rett syndrome: a complex disorder with simple roots.Nat Rev Genet. 2015 May;16(5):261-75. doi: 10.1038/nrg3897. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Nat Rev Genet. 2015. PMID: 25732612 Review.
-
Amplification of neurotoxic HTTex1 assemblies in human neurons.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Nov;159:105517. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105517. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 34563643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hacker H, Karin M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci STKE. 2006;357:re13. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence T, Bebien M, Liu GY, Nizet V, Karin M. IKKalpha limits macrophage NF-kappaB activation and contributes to the resolution of inflammation. Nature. 2005;434:1138–1143. - PubMed
-
- Chariot A. The NF-kappaB-independent functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19:404–413. - PubMed
-
- Jepsen K, Solum D, Zhou T, McEvilly RJ, Kim HJ, et al. SMRT-mediated repression of an H3K27 demethylase in progression from neural stem cell to neuron. Nature. 2007;450:415–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

