The interaction between the yeast telomerase RNA and the Est1 protein requires three structural elements
- PMID: 22847816
- PMCID: PMC3425775
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.034447.112
The interaction between the yeast telomerase RNA and the Est1 protein requires three structural elements
Abstract
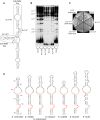
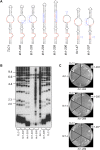
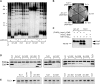
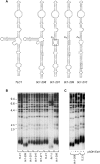
In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the telomerase enzyme is composed of a 1.3-kb TLC1 RNA that forms a complex with Est2 (the catalytic subunit) and two regulatory proteins, Est1 and Est3. Previous work has identified a conserved 5-nt bulge, present in a long helical arm of TLC1, which mediates binding of Est1 to TLC1. However, increased expression of Est1 can bypass the consequences of removal of this RNA bulge, indicating that there are additional binding site(s) for Est1 on TLC1. We report here that a conserved single-stranded internal loop immediately adjacent to the bulge is also required for the Est1-RNA interaction; furthermore, a TLC1 variant that lacks this internal loop but retains the bulge cannot be suppressed by Est1 overexpression, arguing that the internal loop may be a more critical element for Est1 binding. An additional structural feature consisting of a single-stranded region at the base of the helix containing the bulge and internal loop also contributes to recognition of TLC1 by Est1, potentially by providing flexibility to this helical arm. Association of Est1 with each of these TLC1 motifs was assessed using a highly sensitive biochemical assay that simultaneously monitors the relative levels of the Est1 and Est2 proteins in the telomerase complex. The identification of three elements of TLC1 that are required for Est1 association provides a detailed view of this particular protein-RNA interaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A second essential function of the Est1-binding arm of yeast telomerase RNA.RNA. 2015 May;21(5):862-76. doi: 10.1261/rna.049379.114. Epub 2015 Mar 3. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25737580 Free PMC article.
-
The Est1 subunit of yeast telomerase binds the Tlc1 telomerase RNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Mar;20(6):1947-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.6.1947-1955.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10688642 Free PMC article.
-
The principal role of Ku in telomere length maintenance is promotion of Est1 association with telomeres.Genetics. 2014 Aug;197(4):1123-36. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.164707. Epub 2014 May 30. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24879463 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Telomerase RNA Flexibly Scaffolds Protein Subunits: Results and Repercussions.Molecules. 2020 Jun 14;25(12):2750. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122750. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32545864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of telomerase by telomeric proteins.Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:177-208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.071403.160049. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15189140 Review.
Cited by
-
A yeast telomerase complex containing the Est1 recruitment protein is assembled early in the cell cycle.Biochemistry. 2013 Feb 19;52(7):1131-3. doi: 10.1021/bi3015218. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23390975 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated assembly and disassembly of the yeast telomerase quaternary complex.Genes Dev. 2014 Oct 1;28(19):2077-89. doi: 10.1101/gad.246256.114. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 25240060 Free PMC article.
-
Normal telomere length maintenance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires nuclear import of the ever shorter telomeres 1 (Est1) protein via the importin alpha pathway.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Aug;13(8):1036-50. doi: 10.1128/EC.00115-14. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24906415 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast telomerase module for telomere recruitment requires a specific RNA architecture.RNA. 2018 Aug;24(8):1067-1079. doi: 10.1261/rna.066696.118. Epub 2018 May 18. RNA. 2018. PMID: 29777050 Free PMC article.
-
A second essential function of the Est1-binding arm of yeast telomerase RNA.RNA. 2015 May;21(5):862-76. doi: 10.1261/rna.049379.114. Epub 2015 Mar 3. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25737580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchi A, Negrini S, Shore D 2004. Delivery of yeast telomerase to a DNA break depends on the recruitment functions of Cdc13 and Est1. Mol Cell 16: 139–146 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
