Roles of ceramide and sphingolipids in pancreatic β-cell function and dysfunction
- PMID: 22847494
- PMCID: PMC3442815
- DOI: 10.4161/isl.20102
Roles of ceramide and sphingolipids in pancreatic β-cell function and dysfunction
Abstract
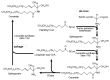
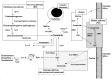
Recent technical advances have re-invigorated the study of sphingolipid metabolism in general, and helped to highlight the varied and important roles that sphingolipids play in pancreatic β-cells. Sphingolipid metabolites such as ceramide, glycosphingolipids, sphingosine 1-phosphate and gangliosides modulate many β-cell signaling pathways and processes implicated in β-cell diabetic disease such as apoptosis, β-cell cytokine secretion, ER-to-golgi vesicular trafficking, islet autoimmunity and insulin gene expression. They are particularly relevant to lipotoxicity. Moreover, the de novo synthesis of sphingolipids occurs on many subcellular membranes, in parallel to secretory vesicle formation, traffic and granule maturation events. Indeed, the composition of the plasma membrane, determined by the activity of neutral sphingomyelinases, affects β-cell excitability and potentially insulin exocytosis while another glycosphingolipid, sulfatide, determines the stability of insulin crystals in granules. Most importantly, sphingolipid metabolism on internal membranes is also strongly implicated in regulating β-cell apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting sphingolipid metabolism in the treatment of obesity/type 2 diabetes.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015;19(8):1037-50. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1028359. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 25814122 Review.
-
An overview of sphingolipid metabolism: from synthesis to breakdown.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;688:1-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6741-1_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20919643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids as a Culprit of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 18;12:635175. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635175. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33815291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of de novo ceramide synthesis by sirtuin-1 improves beta-cell function and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes.Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Sep 21;120(11):1265-1278. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvae100. Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 38739545
-
Sphingolipids and cancer: ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in the regulation of cell death and drug resistance.Future Oncol. 2010 Oct;6(10):1603-24. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.116. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21062159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Intestinal Microbiota-Farnesoid X Receptor Axis Modulates Metabolic Disease.Gastroenterology. 2016 Nov;151(5):845-859. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.08.057. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27639801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of sphingolipid metabolism augments ceramide-induced autophagy in preeclampsia.Autophagy. 2015 Apr 3;11(4):653-69. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034414. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25853898 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-impaired transcription factor expression and insulin secretion in transplanted human islets.J Clin Invest. 2016 May 2;126(5):1857-70. doi: 10.1172/JCI83657. Epub 2016 Apr 11. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27064285 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipid subtypes differentially control proinsulin processing and systemic glucose homeostasis.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Jan;25(1):20-29. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-01027-2. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36543979 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Sphingolipids in Insulin Resistance, Diabetes and Associated Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 13;24(18):14015. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814015. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tettamanti G. Ganglioside/glycosphingolipid turnover: new concepts. Glycoconj J. 2004;20:301–17. doi: 10.1023/B:GLYC.0000033627.02765.cc. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hanada K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1632:16–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
