Gene expression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis putative transcription factors whiB1-7 in redox environments
- PMID: 22829866
- PMCID: PMC3400605
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037516
Gene expression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis putative transcription factors whiB1-7 in redox environments
Abstract
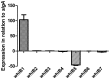
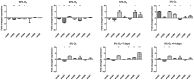
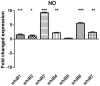
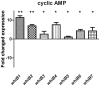
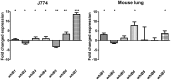
The seven WhiB proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) are widely believed to be redox-sensing transcription factors due to their binding of iron-sulfur clusters and similarities to DNA binding proteins. Here, we explored the nature of this hypothesized relationship. We exposed M.tb to physiologic conditions such as gradual hypoxia, nitric oxide (NO), cyclic AMP and in vivo conditions, and measured transcription of the whiB genes. We found whiB3 to be induced both by hypoxia and NO, whiB7 to be induced in macrophage-like cells, and whiB4 to be induced in mouse lung. Cyclic AMP induced whiB1,-2, -4, -6 and -7. Our data indicate that the M.tb whiB genes are induced independently by various stimuli which may add versatility to their suggested redox-sensing properties.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into redox sensing metalloproteins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Inorg Biochem. 2014 Apr;133:118-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Inorg Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24314844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies on structural and functional divergence among seven WhiB proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv.FEBS J. 2009 Jan;276(1):76-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06755.x. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19016840
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis WhiB1 is an essential DNA-binding protein with a nitric oxide-sensitive iron-sulfur cluster.Biochem J. 2010 Dec 15;432(3):417-27. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101440. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20929442 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of DNA binding by the WhiB-like transcription factor WhiB3 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jun;299(6):104777. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104777. Epub 2023 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37142222 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of redox sensing in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Oct 15;53(8):1625-41. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22921590 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into redox sensing metalloproteins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Inorg Biochem. 2014 Apr;133:118-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Inorg Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24314844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RegX3 Activates whiB3 Under Acid Stress and Subverts Lysosomal Trafficking of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a WhiB3-Dependent Manner.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 16;11:572433. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.572433. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33042081 Free PMC article.
-
A Nonsynonymous SNP Catalog of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Virulence Genes and Its Use for Detecting New Potentially Virulent Sublineages.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 Apr 1;9(4):887-899. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx053. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28338924 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome Sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strain E186hv of Beijing B0/W Lineage with Reduced Virulence.Genome Announc. 2015 May 7;3(3):e00403-15. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00403-15. Genome Announc. 2015. PMID: 25953188 Free PMC article.
-
WhiB-like proteins: Diversity of structure, function and mechanism.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024 Oct;1871(7):119787. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119787. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38879133 Review.
References
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis control: WHO report. 2011.
-
- Rustad TR, Sherrid AM, Minch KJ, Sherman DR. Hypoxia: a window into Mycobacterium tuberculosis latency. Cell Microbiol. 2009;11:1151–1159. - PubMed
-
- Soliveri JA, Gomez J, Bishai WR, Chater KF. Multiple paralogous genes related to the Streptomyces coelicolor developmental regulatory gene whiB are present in Streptomyces and other actinomycetes. Microbiology 146 (Pt. 2000;2):333–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

