The extracellular and transmembrane domains of the γC and interleukin (IL)-13 receptor α1 chains, not their cytoplasmic domains, dictate the nature of signaling responses to IL-4 and IL-13
- PMID: 22829596
- PMCID: PMC3442527
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.348896
The extracellular and transmembrane domains of the γC and interleukin (IL)-13 receptor α1 chains, not their cytoplasmic domains, dictate the nature of signaling responses to IL-4 and IL-13
Abstract
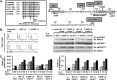
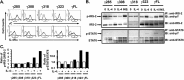
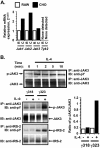
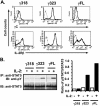
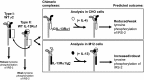
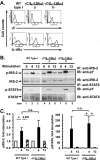
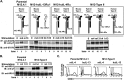
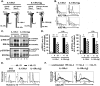
Previously, we demonstrated that the γC subunit of type I IL-4 receptor was required for robust tyrosine phosphorylation of the downstream adapter protein, IRS-2, correlating with the expression of genes (ArgI, Retnla, and Chi3l3) characteristic of alternatively activated macrophages. We located an I4R-like motif (IRS-2 docking sequence) in the γC cytoplasmic domain but not in the IL-13Rα1. Thus, we predicted that the γC tail directed enhanced IRS-2 phosphorylation. To test this, IL-4 signaling responses were examined in a mutant of the key I4R motif tyrosine residue (Y325F) and different γC truncation mutants (γ285, γ308, γ318, γ323, and γFULL LENGTH (FL)) co-expressed in L-cells or CHO cells with wild-type (WT) IL-4Rα. Surprisingly, IRS-1 phosphorylation was not diminished in Y325F L-cell mutants suggesting Tyr-325 was not required for the robust insulin receptor substrate response. IRS-2, STAT6, and JAK3 phosphorylation was observed in CHO cells expressing γ323 and γFL but not in γ318 and γ285 mutants. In addition, when CHO cells expressed γ318, γ323, or γFL with IL-2Rβ, IL-2 induced phospho-STAT5 only in the γ323 and γFL clones. Our data suggest that a smaller (5 amino acid) interval than previously determined is necessary for JAK3 activation/γC-mediated signaling in response to IL-4 and IL-2. Chimeric receptor chains of the γC tail fused to the IL-13Rα1 extracellular and transmembrane domain did not elicit robust IRS-2 phosphorylation in response to IL-13 suggesting that the extracellular/transmembrane domains of the IL-4/IL-13 receptor, not the cytoplasmic domains, control signaling efficiency. Understanding this pathway fully will lead to rational drug design for allergic disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A role for the insulin-interleukin (IL)-4 receptor motif of the IL-4 receptor alpha-chain in regulating activation of the insulin receptor substrate 2 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 pathways. Analysis by mutagenesis.J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 17;273(16):9898-905. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.16.9898. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9545332
-
Interleukin-13 receptor alpha' but not alpha chain: a functional component of interleukin-4 receptors.Blood. 1998 May 15;91(10):3884-91. Blood. 1998. PMID: 9573026
-
IL-4 receptor alpha is an important modulator of IL-4 and IL-13 receptor binding: implications for the development of therapeutic targets.J Immunol. 2006 Jun 15;176(12):7456-61. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7456. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16751391
-
IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: an evolving web.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003 Apr;111(4):677-90; quiz 691. doi: 10.1067/mai.2003.1333. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12704343 Review.
-
IL-4/IL-13 signaling beyond JAK/STAT.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000 Jun;105(6 Pt 1):1063-70. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.107604. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10856136 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifarious determinants of cytokine receptor signaling specificity.Adv Immunol. 2014;121:1-39. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800100-4.00001-5. Adv Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24388212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuning cytokine receptor signaling by re-orienting dimer geometry with surrogate ligands.Cell. 2015 Mar 12;160(6):1196-208. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cell. 2015. PMID: 25728669 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting interleukin 4 and interleukin 13: a novel therapeutic approach in bullous pemphigoid.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):1156-1170. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2188487. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 36999962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The differential expression of IL-4 and IL-13 and its impact on type-2 immunity.Cytokine. 2015 Sep;75(1):25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26073683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping Determinants of Cytokine Signaling via Protein Engineering.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 27;9:2143. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02143. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319612 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnes P. J. (2011) Pathophysiology of allergic inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 242, 31–50 - PubMed
-
- Al-Muhsen S., Johnson J. R., Hamid Q. (2011) Remodeling in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 128, 451–462 - PubMed
-
- Chatila T. A. (2004) Interleukin-4 receptor signaling pathways in asthma pathogenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 10, 493–499 - PubMed
-
- Lowenthal J. W., Castle B. E., Christiansen J., Schreurs J., Rennick D., Arai N., Hoy P., Takebe Y., Howard M. (1988) Expression of high affinity receptors for murine interleukin 4 (BSF-1) on hemopoietic and nonhemopoietic cells. J. Immunol. 140, 456–464 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

