A NAC transcription factor and SNI1 cooperatively suppress basal pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 22826500
- PMCID: PMC3467076
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks683
A NAC transcription factor and SNI1 cooperatively suppress basal pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
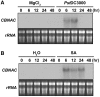
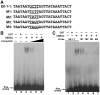
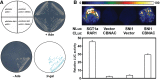
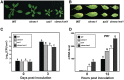
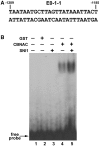
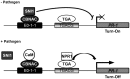
Transcriptional repression of pathogen defense-related genes is essential for plant growth and development. Several proteins are known to be involved in the transcriptional regulation of plant defense responses. However, mechanisms by which expression of defense-related genes are regulated by repressor proteins are poorly characterized. Here, we describe the in planta function of CBNAC, a calmodulin-regulated NAC transcriptional repressor in Arabidopsis. A T-DNA insertional mutant (cbnac1) displayed enhanced resistance to a virulent strain of the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae DC3000 (PstDC3000), whereas resistance was reduced in transgenic CBNAC overexpression lines. The observed changes in disease resistance were correlated with alterations in pathogenesis-related protein 1 (PR1) gene expression. CBNAC bound directly to the PR1 promoter. SNI1 (suppressor of nonexpressor of PR genes1, inducible 1) was identified as a CBNAC-binding protein. Basal resistance to PstDC3000 and derepression of PR1 expression was greater in the cbnac1 sni1 double mutant than in either cbnac1 or sni1 mutants. SNI1 enhanced binding of CBNAC to its cognate PR1 promoter element. CBNAC and SNI1 are hypothesized to work as repressor proteins in the cooperative suppression of plant basal defense.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA repair proteins are directly involved in regulation of gene expression during plant immune response.Cell Host Microbe. 2011 Feb 17;9(2):115-24. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.01.011. Cell Host Microbe. 2011. PMID: 21320694
-
Overexpression of Arabidopsis ACBP3 enhances NPR1-dependent plant resistance to Pseudomonas syringe pv tomato DC3000.Plant Physiol. 2011 Aug;156(4):2069-81. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.176933. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21670223 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive structure-function analysis of Arabidopsis SNI1 defines essential regions and transcriptional repressor activity.Plant Cell. 2006 Jul;18(7):1750-65. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.039677. Epub 2006 Jun 9. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 16766691 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylene Response Factor ERF11 Activates BT4 Transcription to Regulate Immunity to Pseudomonas syringae.Plant Physiol. 2019 Jun;180(2):1132-1151. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01209. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30926656 Free PMC article.
-
Actin branches out to link pathogen perception and host gene regulation.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Mar;8(3):e23468. doi: 10.4161/psb.23468. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23333960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved oomycete effector RxLR23 triggers plant defense responses by targeting ERD15La to release NbNAC68.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 27;15(1):6336. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50782-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39068146 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling in Plant Immunity--At the Crossroad of Life and Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 5;16(11):26582-98. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125964. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26556351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription Factor Functional Protein-Protein Interactions in Plant Defense Responses.Proteomes. 2014 Mar 4;2(1):85-106. doi: 10.3390/proteomes2010085. Proteomes. 2014. PMID: 28250372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in calcium/calmodulin-mediated signaling with an emphasis on plant-microbe interactions.Plant Physiol. 2013 Oct;163(2):531-42. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.220780. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24014576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three Rice NAC Transcription Factors Heteromerize and Are Associated with Seed Size.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Nov 7;7:1638. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01638. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27872632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dangl JL, Jones JD. Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature. 2001;411:826–833. - PubMed
-
- Durrant WE, Dong X. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004;42:185–209. - PubMed
-
- Glazebrook J. Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005;43:205–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

