The R-Ras/RIN2/Rab5 complex controls endothelial cell adhesion and morphogenesis via active integrin endocytosis and Rac signaling
- PMID: 22825554
- PMCID: PMC3463263
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2012.110
The R-Ras/RIN2/Rab5 complex controls endothelial cell adhesion and morphogenesis via active integrin endocytosis and Rac signaling
Abstract
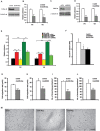
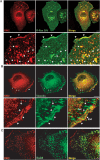
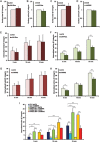
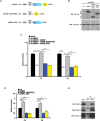
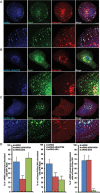
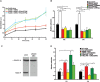
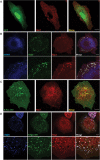
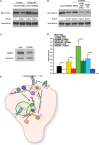
During developmental and tumor angiogenesis, semaphorins regulate blood vessel navigation by signaling through plexin receptors that inhibit the R-Ras subfamily of small GTPases. R-Ras is mainly expressed in vascular cells, where it induces adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) through unknown mechanisms. We identify the Ras and Rab5 interacting protein RIN2 as a key effector that in endothelial cells interacts with and mediates the pro-adhesive and -angiogenic activity of R-Ras. Both R-Ras-GTP and RIN2 localize at nascent ECM adhesion sites associated with lamellipodia. Upon binding, GTP-loaded R-Ras converts RIN2 from a Rab5 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) to an adaptor that first interacts at high affinity with Rab5-GTP to promote the selective endocytosis of ligand-bound/active β1 integrins and then causes the translocation of R-Ras to early endosomes. Here, the R-Ras/RIN2/Rab5 signaling module activates Rac1-dependent cell adhesion via TIAM1, a Rac GEF that localizes on early endosomes and is stimulated by the interaction with both Ras proteins and the vesicular lipid phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate. In conclusion, the ability of R-Ras-GTP to convert RIN2 from a GEF to an adaptor that preferentially binds Rab5-GTP allows the triggering of the endocytosis of ECM-bound/active β1 integrins and the ensuing funneling of R-Ras-GTP toward early endosomes to elicit the pro-adhesive and TIAM1-mediated activation of Rac1.
Figures
Comment in
-
A tale of three GTPases and a RIN in endothelial cell adhesion.Cell Res. 2012 Oct;22(10):1426-8. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.118. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22890385 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
A tale of three GTPases and a RIN in endothelial cell adhesion.Cell Res. 2012 Oct;22(10):1426-8. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.118. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22890385 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the Ras-Ras-activated Rab5 guanine nucleotide exchange factor RIN2-Rab5 pathway in the hepatocyte growth factor-induced endocytosis of E-cadherin.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 14;281(15):10598-609. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510531200. Epub 2006 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16423831
-
RIN3: a novel Rab5 GEF interacting with amphiphysin II involved in the early endocytic pathway.J Cell Sci. 2003 Oct 15;116(Pt 20):4159-68. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00718. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12972505
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
-
[Effectors of GTPase Rab5 in endocytosis and signal transduction].Postepy Biochem. 2009;55(2):171-80. Postepy Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19824473 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
RIT1 controls actin dynamics via complex formation with RAC1/CDC42 and PAK1.PLoS Genet. 2018 May 7;14(5):e1007370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007370. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29734338 Free PMC article.
-
Rab'ing tumor cell migration and invasion: focal adhesion disassembly driven by Rab5.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(2):84-7. doi: 10.4161/cam.28510. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 24727246 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic Counterbalance of RAC1-YAP/OB-Cadherin Coordinates Tissue Spreading with Stem Cell Fate Patterning.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 8;8(10):2004000. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004000. eCollection 2021 May. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34026448 Free PMC article.
-
The availability of the embryonic TGF-β protein Nodal is dynamically regulated during glioblastoma multiforme tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell Int. 2016 Jun 17;16:46. doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0324-3. eCollection 2016. Cancer Cell Int. 2016. PMID: 27330409 Free PMC article.
-
Spatially restricted G protein-coupled receptor activity via divergent endocytic compartments.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 14;289(7):3960-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526350. Epub 2013 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24375413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fraisl P, Mazzone M, Schmidt T, Carmeliet P. Regulation of angiogenesis by oxygen and metabolism. Dev Cell. 2009;16:167–179. - PubMed
-
- Jones EA, le Noble F, Eichmann A. What determines blood vessel structure? Genetic prespecification vs. hemodynamics. Physiology (Bethesda) 2006;21:388–395. - PubMed
-
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–478. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Lessons from multidisciplinary translational trials on anti-angiogenic therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005;307:58–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

