Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 22824096
- PMCID: PMC3443459
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-5-11
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
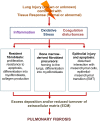
Pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic lung disease characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) and remodeling of the lung architecture. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is considered the most common and severe form of the disease, with a median survival of approximately three years and no proven effective therapy. Despite the fact that effective treatments are absent and the precise mechanisms that drive fibrosis in most patients remain incompletely understood, an extensive body of scientific literature regarding pulmonary fibrosis has accumulated over the past 35 years. In this review, we discuss three broad areas which have been explored that may be responsible for the combination of altered lung fibroblasts, loss of alveolar epithelial cells, and excessive accumulation of ECM: inflammation and immune mechanisms, oxidative stress and oxidative signaling, and procoagulant mechanisms. We discuss each of these processes separately to facilitate clarity, but certainly significant interplay will occur amongst these pathways in patients with this disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathogenetic pathways and novel pharmacotherapeutic targets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2007;20(5):453-61. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2006.01.002. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 16516512 Review.
-
Extracellular matrix remodeling in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It is the 'bed' that counts and not 'the sleepers'.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2017 Apr;11(4):299-309. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2017.1300533. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2017. PMID: 28274188 Review.
-
Revealing the pathogenic and aging-related mechanisms of the enigmatic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. an integral model.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 May 15;189(10):1161-72. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201312-2221PP. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24641682
-
Epithelium-dependent profibrotic milieu in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: current status and future directions.Clin Respir J. 2016 Mar;10(2):133-41. doi: 10.1111/crj.12190. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Clin Respir J. 2016. PMID: 25047066 Review.
-
Latest progress on the molecular mechanisms of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Dec;47(12):9811-9820. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06000-6. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33230784 Review.
Cited by
-
Heavy metals: toxicity and human health effects.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Nov 20. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03903-2. Online ahead of print. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39567405 Review.
-
Personalized in silico model for radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis.J R Soc Interface. 2024 Nov;21(220):20240525. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2024.0525. Epub 2024 Nov 13. J R Soc Interface. 2024. PMID: 39532130 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Non-rodent animal model of hydrochloric acid-induced acute and chronic lung injury.Respir Res. 2024 Oct 29;25(1):390. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03022-7. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39472954 Free PMC article.
-
Hemin attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice by regulating the TGF-β1/MAPK and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α/HO-1/NF-κB pathways.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 1;28(6):559-568. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.6.559. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39467719 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Diseases.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 13;16(16):2837. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162837. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takishima T, Shimura S. In: Basic and clinical aspects of pulmonary fibrosis. Takishima T, editor. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL; 1994. Definition and Classification of Pulmonary Fibrosis; pp. 293–303.
-
- Orr CR, Jacobs WF. Pulmonary Fibrosis. Radiology. 1926;7:318–325.
-
- Hamman L, Rich A. Acute diffuse interstitial fibrosis of the lungs. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1944;74:177–212.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

