Hypoxic preconditioning improves survival of cardiac progenitor cells: role of stromal cell derived factor-1α-CXCR4 axis
- PMID: 22815687
- PMCID: PMC3399836
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037948
Hypoxic preconditioning improves survival of cardiac progenitor cells: role of stromal cell derived factor-1α-CXCR4 axis
Abstract
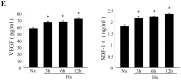
Background: Cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) have been shown to be suitable in stem cell therapy for resurrecting damaged myocardium, but poor retention of transplanted cells in the ischemic myocardium causes ineffective cell therapy. Hypoxic preconditioning of cells can increase the expression of CXCR4 and pro-survival genes to promote better cell survival; however, it is unknown whether hypoxia preconditioning will influence the survival and retention of CPCs via the SDF-1α/CXCR4 axis.
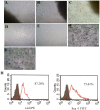
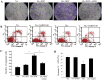
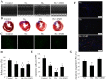
Methods and results: CPCs were isolated from adult mouse hearts and purified by magnetic activated cell sorting using c-kit magnetic beads. These cells were cultured at various times in either normoxic or hypoxic conditions, and cell survival was analyzed using flow cytometry and the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), CXCR4, phosphorylated Akt and Bcl-2 were measured by Western blot. Results showed that the expression of pro-survival genes significantly increased after hypoxia treatment, especially in cells cultured in hypoxic conditions for six hours. Upon completion of hypoxia preconditioning from c-kit+ CPCs for six hours, the anti-apoptosis, migration and cardiac repair potential were evaluated. Results showed a significant enhancement in anti-apoptosis and migration in vitro, and better survival and cardiac function after being transplanted into acute myocardial infarction (MI) mice in vivo. The beneficial effects induced by hypoxia preconditioning of c-kit+ CPCs could largely be blocked by the addition of CXCR4 selective antagonist AMD3100.
Conclusions: Hypoxic preconditioning may improve the survival and retention of c-kit+ CPCs in the ischemic heart tissue through activating the SDF-1α/CXCR4 axis and the downstream anti-apoptosis pathway. Strategies targeting this aspect may enhance the effectiveness of cell-based cardiac regenerative therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxic preconditioning enhances the benefit of cardiac progenitor cell therapy for treatment of myocardial infarction by inducing CXCR4 expression.Circ Res. 2009 May 22;104(10):1209-16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.197723. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19407239 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of SDF-1α enhanced migration and engraftment of cardiac stem cells and reduced infarcted size via CXCR4/PI3K pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e43922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043922. Epub 2012 Sep 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984452 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of cardiac progenitor cells marker c-kit by stromal cell derived factor-1α.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 24;8(7):e69134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069134. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2021 Feb 12;16(2):e0247094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247094. PMID: 23894420 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Genetically manipulated progenitor/stem cells restore function to the infarcted heart via the SDF-1α/CXCR4 signaling pathway.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;111:265-84. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-398459-3.00012-5. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22917235 Review.
-
The SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in stem cell preconditioning.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Jun 1;94(3):400-7. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs132. Epub 2012 Mar 26. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22451511 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute preconditioning of cardiac progenitor cells with hydrogen peroxide enhances angiogenic pathways following ischemia-reperfusion injury.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Sep 1;22(17):2414-24. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0673. Epub 2013 May 25. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23544670 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic Preconditioning Inhibits Hypoxia-induced Apoptosis of Cardiac Progenitor Cells via the PI3K/Akt-DNMT1-p53 Pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 4;6:30922. doi: 10.1038/srep30922. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27488808 Free PMC article.
-
NT3P75-2 gene-modified bone mesenchymal stem cells improve neurological function recovery in mouse TBI model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Oct 24;10(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1428-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31651375 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic preconditioning effect on stromal cells derived factor-1 and C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 expression in Wistar rat's (Rattus norvegicus) bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (in vitro study).Vet World. 2018 Jul;11(7):965-970. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.965-970. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Vet World. 2018. PMID: 30147267 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac-derived stem cell-based therapy for heart failure: progress and clinical applications.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013 Mar;238(3):294-300. doi: 10.1177/1535370213477982. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013. PMID: 23598975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kajstura J, Gurusamy N, Ogo’rek B, Goichberg P, Clavo-Rondon C, et al. Myocyte Turnover in the Aging Human Heart. Circ Res. 2010;107:1374–1386. - PubMed
-
- Beltrami AP, Barlucchi L, Torella D, Baker M, Limana F, et al. Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration. Cell. 2003;114:763–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

