A meta-analysis reveals the commonalities and differences in Arabidopsis thaliana response to different viral pathogens
- PMID: 22808182
- PMCID: PMC3395709
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040526
A meta-analysis reveals the commonalities and differences in Arabidopsis thaliana response to different viral pathogens
Abstract
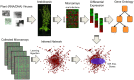
Understanding the mechanisms by which plants trigger host defenses in response to viruses has been a challenging problem owing to the multiplicity of factors and complexity of interactions involved. The advent of genomic techniques, however, has opened the possibility to grasp a global picture of the interaction. Here, we used Arabidopsis thaliana to identify and compare genes that are differentially regulated upon infection with seven distinct (+)ssRNA and one ssDNA plant viruses. In the first approach, we established lists of genes differentially affected by each virus and compared their involvement in biological functions and metabolic processes. We found that phylogenetically related viruses significantly alter the expression of similar genes and that viruses naturally infecting Brassicaceae display a greater overlap in the plant response. In the second approach, virus-regulated genes were contextualized using models of transcriptional and protein-protein interaction networks of A. thaliana. Our results confirm that host cells undergo significant reprogramming of their transcriptome during infection, which is possibly a central requirement for the mounting of host defenses. We uncovered a general mode of action in which perturbations preferentially affect genes that are highly connected, central and organized in modules.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of senescence-associated Dark-inducible (DIN) genes during infection contributes to enhanced susceptibility to plant viruses.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Jan;17(1):3-15. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12257. Epub 2015 May 4. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 25787925 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Global Transcriptome Changes in Response to South African Cassava Mosaic Virus [ZA-99] Infection in Susceptible Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e67534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067534. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826319 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse RNA viruses elicit the expression of common sets of genes in susceptible Arabidopsis thaliana plants.Plant J. 2003 Jan;33(2):271-83. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01625.x. Plant J. 2003. PMID: 12535341
-
A systems biology approach to the evolution of plant-virus interactions.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2011 Aug;14(4):372-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2011.03.013. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21458360 Review.
-
Genetics of plant virus resistance.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2005;43:581-621. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.011205.141140. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2005. PMID: 16078896 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of senescence-associated Dark-inducible (DIN) genes during infection contributes to enhanced susceptibility to plant viruses.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Jan;17(1):3-15. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12257. Epub 2015 May 4. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 25787925 Free PMC article.
-
Hexanoic Acid Treatment Prevents Systemic MNSV Movement in Cucumis melo Plants by Priming Callose Deposition Correlating SA and OPDA Accumulation.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Oct 20;8:1793. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01793. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29104580 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression network analysis of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) genes with stress-responsive genes in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals 13 key regulators.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 8;10(1):21480. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77746-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33293553 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative transcriptional changes associated with chlorosis severity in mosaic leaves of tobacco plants infected with Cucumber mosaic virus.Mol Plant Pathol. 2014 Apr;15(3):242-54. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12081. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24745045 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Cucumis sativus infected by Cucurbit chlorotic yellows virus.Virol J. 2017 Feb 2;14(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0690-z. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28148297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dodds PN, Rathjen JP. Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:539–548. - PubMed
-
- Maule A, Leh V, Lederer C. The dialogue between viruses and hosts in compatible interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002;5:279–284. - PubMed
-
- Whitham SA, Quan S, Chang HS, Cooper B, Estes B, et al. Diverse RNA viruses elicit the expression of common sets of genes in susceptible Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Plant J. 2003;33:271–283. - PubMed

