Development and validation of genic-SSR markers in sesame by RNA-seq
- PMID: 22800194
- PMCID: PMC3428654
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-316
Development and validation of genic-SSR markers in sesame by RNA-seq
Abstract
Background: Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) is one of the most important oil crops; however, a lack of useful molecular markers hinders current genetic research. We performed transcriptome sequencing of samples from different sesame growth and developmental stages, and mining of genic-SSR markers to identify valuable markers for sesame molecular genetics research.
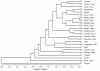
Results: In this study, 75 bp and 100 bp paired-end RNA-seq was used to sequence 24 cDNA libraries, and 42,566 uni-transcripts were assembled from more than 260 million filtered reads. The total length of uni-transcript sequences was 47.99 Mb, and 7,324 SSRs (SSRs ≥15 bp) and 4,440 SSRs (SSRs ≥18 bp) were identified. On average, there was one genic-SSR per 6.55 kb (SSRs ≥15 bp) or 10.81 kb (SSRs ≥18 bp). Among perfect SSRs (≥18 bp), di-nucleotide motifs (48.01%) were the most abundant, followed by tri- (20.96%), hexa- (25.37%), penta- (2.97%), tetra- (2.12%), and mono-nucleotides (0.57%). The top four motif repeats were (AG/CT)n [1,268 (34.51%)], (CA/TG)n [281 (7.65%)], (AT/AT)n [215 (5.85%)], and (GAA/TTC)n [131 (3.57%)]. A total of 2,164 SSR primer pairs were identified in the 4,440 SSR-containing sequences (≥18 bp), and 300 SSR primer pairs were randomly chosen for validation. These SSR markers were amplified and validated in 25 sesame accessions (24 cultivated accessions, one wild species). 276 (92.0%) primer pairs yielded PCR amplification products in 24 cultivars. Thirty two primer pairs (11.59%) exhibited polymorphisms. Moreover, 203 primer pairs (67.67%) yielded PCR amplicons in the wild accession and 167 (60.51%) were polymorphic between species. A UPGMA dendrogram based on genetic similarity coefficients showed that the correlation between genotype and geographical source was low and that the genetic basis of sesame in China is narrow, as previously reported. The 32 polymorphic primer pairs were validated using an F2 mapping population; 18 primer pairs exhibited polymorphisms between the parents, and 14 genic-SSRs could be integrated into 9 main linkage groups.
Conclusions: 2,164 genic-SSR markers have been developed in sesame using transcriptome sequencing. 276 of 300 validated primer pairs successfully yielded PCR amplicons in 24 cultivated sesame accessions. These markers increase current SSR marker resources and will greatly benefit genetic diversity, qualitative and quantitative trait mapping and marker-assisted selection studies in sesame.
Figures



Similar articles
-
De novo Assembly, Characterization of Immature Seed Transcriptome and Development of Genic-SSR Markers in Black Gram [Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper].PLoS One. 2015 Jun 4;10(6):e0128748. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128748. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26042595 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterization of genic-SSR markers from different Asia lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) types by RNA-seq.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Sep 22;14(3):11171-84. doi: 10.4238/2015.September.22.11. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 26400348
-
Characterization of flower-bud transcriptome and development of genic SSR markers in Asian lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.).PLoS One. 2014 Nov 7;9(11):e112223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112223. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25379700 Free PMC article.
-
Mining and Development of Novel SSR Markers Using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Data in Plants.Molecules. 2018 Feb 13;23(2):399. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020399. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29438290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streamlining of Simple Sequence Repeat Data Mining Methodologies and Pipelines for Crop Scanning.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 19;13(18):2619. doi: 10.3390/plants13182619. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catalyzing plant science research with RNA-seq.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Apr 1;4:66. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00066. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23554602 Free PMC article.
-
PSR: polymorphic SSR retrieval.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Oct 1;8:525. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1474-4. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 26428628 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and genetic diversity assessment of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) accessions differing in origin.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2015 Oct;21(4):519-29. doi: 10.1007/s12298-015-0322-2. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2015. PMID: 26600678 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Oilseed Crop Sesamum indicum Enters the "Omics" Era.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jun 30;8:1154. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01154. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28713412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Diversity, Population Structure, and Linkage Disequilibrium of an Association-Mapping Panel Revealed by Genome-Wide SNP Markers in Sesame.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jul 6;8:1189. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01189. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28729877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashri A. Sesame breeding. Plant Breeding Review. 1998;16:179–228.
-
- Bhat KV, Babrekar PP, Lakhanpaul S. Study of genetic diversity in Indian and exotic sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) germplasm using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Euphytical. 1999;110:21–33.
-
- Ercan AG, Taskin M, Turgut K. Analysis of genetic diversity in Turkish sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) populations using RAPD markers. Genet Res Crop Evol. 2004;51
-
- Kim DH, Zur G, Danin-Poleg Y, Lee S, Shim K, Kang C, Kashi Y. Genetic relationships of sesame germplasm collection as revealed by inter-simple sequence repeats. Plant Breed. 2002;121:259–262.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

