Small molecule activators of the heat shock response: chemical properties, molecular targets, and therapeutic promise
- PMID: 22799889
- PMCID: PMC3472121
- DOI: 10.1021/tx300264x
Small molecule activators of the heat shock response: chemical properties, molecular targets, and therapeutic promise
Abstract
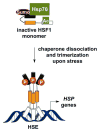
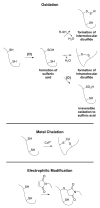
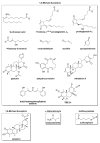
All cells have developed various mechanisms to respond and adapt to a variety of environmental challenges, including stresses that damage cellular proteins. One such response, the heat shock response (HSR), leads to the transcriptional activation of a family of molecular chaperone proteins that promote proper folding or clearance of damaged proteins within the cytosol. In addition to its role in protection against acute insults, the HSR also regulates lifespan and protects against protein misfolding that is associated with degenerative diseases of aging. As a result, identifying pharmacological regulators of the HSR has become an active area of research in recent years. Here, we review progress made in identifying small molecule activators of the HSR, what cellular targets these compounds interact with to drive response activation, and how such molecules may ultimately be employed to delay or reverse protein misfolding events that contribute to a number of diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Underlying mechanisms and chemical/biochemical therapeutic approaches to ameliorate protein misfolding neurodegenerative diseases.Biofactors. 2017 Nov;43(6):737-759. doi: 10.1002/biof.1264. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Biofactors. 2017. PMID: 26899445 Review.
-
The heat shock response and small molecule regulators.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Dec 15;226:113846. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113846. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34563965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transportable, Chemical Genetic Methodology for the Small Molecule-Mediated Inhibition of Heat Shock Factor 1.ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Jan 15;11(1):200-10. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00740. Epub 2015 Nov 19. ACS Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26502114 Free PMC article.
-
The heat-shock response: regulation and function of heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones.Essays Biochem. 1997;32:17-29. Essays Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9493008 Review.
-
Contesting the dogma of an age-related heat shock response impairment: implications for cardiac-specific age-related disorders.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Jul 15;23(14):3641-56. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu073. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24556212 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
HIF1, HSF1, and NRF2: Oxidant-Responsive Trio Raising Cellular Defenses and Engaging Immune System.Chem Res Toxicol. 2022 Oct 17;35(10):1690-1700. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00131. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35948068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of HSF1-Activated Pathways as Potential Next-Generation Anticancer Therapeutics.Molecules. 2018 Oct 24;23(11):2757. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112757. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30356024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring of the Heat Shock Response with a Real-Time Luciferase Reporter.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2693:1-11. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3342-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37540422
-
Comparative interactomes of HSF1 in stress and disease reveal a role for CTCF in HSF1-mediated gene regulation.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100097. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015452. Epub 2020 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33208463 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling Stress-Inducible Phosphorylation of Heat Shock Factor 1 from Its Activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jul;35(14):2530-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00816-14. Epub 2015 May 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25963659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Autreaux B, Toledano MB. ROS as signalling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:813–824. - PubMed
-
- Hur W, Gray NS. Small molecule modulators of antioxidant response pathway. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011;15:162–173. - PubMed
-
- Mori K. Signalling pathways in the unfolded protein response: development from yeast to mammals. J Biochem. 2009;146:743–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

