Slicing-independent RISC activation requires the argonaute PAZ domain
- PMID: 22795694
- PMCID: PMC3604743
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.040
Slicing-independent RISC activation requires the argonaute PAZ domain
Abstract
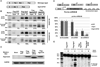
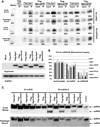
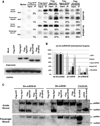
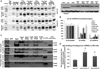
Small RNAs regulate genetic networks through a ribonucleoprotein complex called the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which, in mammals, contains at its center one of four Argonaute proteins (Ago1-Ago4). A key regulatory event in the RNA interference (RNAi) and microRNA (miRNA) pathways is Ago loading, wherein double-stranded small-RNA duplexes are incorporated into RISC (pre-RISC) and then become single-stranded (mature RISC), a process that is not well understood. The Agos contain an evolutionarily conserved PAZ (Piwi/Argonaute/Zwille) domain whose primary function is to bind the 3' end of small RNAs. We created multiple PAZ-domain-disrupted mutant Ago proteins and studied their biochemical properties and biological functionality in cells. We found that the PAZ domain is dispensable for Ago loading of slicing-competent RISC. In contrast, in the absence of slicer activity or slicer-substrate duplex RNAs, PAZ-disrupted Agos bound duplex small interfering RNAs, but were unable to unwind or eject the passenger strand and form functional RISC complexes. We have discovered that the highly conserved PAZ domain plays an important role in RISC activation, providing new mechanistic insights into how miRNAs regulate genes, as well as new insights for future design of miRNA- and RNAi-based therapeutics.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The N domain of Argonaute drives duplex unwinding during RISC assembly.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 10;19(2):145-51. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2232. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22233755
-
Structural determinants of miRNAs for RISC loading and slicer-independent unwinding.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Sep;16(9):953-60. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1630. Epub 2009 Aug 16. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19684602
-
Slicer-independent mechanism drives small-RNA strand separation during human RISC assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 30;43(19):9418-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv937. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26384428 Free PMC article.
-
When Argonaute takes out the ribonuclease sword.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jan;300(1):105499. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105499. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38029964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anatomy of RISC: how do small RNAs and chaperones activate Argonaute proteins?Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Sep;7(5):637-60. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1356. Epub 2016 May 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27184117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational analysis of siRNA recognition by the Ago2 PAZ domain and identification of the determinants of RNA-induced gene silencing.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057140. Epub 2013 Feb 18. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23441235 Free PMC article.
-
In silico molecular docking analysis of the human Argonaute 2 PAZ domain reveals insights into RNA interference.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2013 Jul;27(7):605-14. doi: 10.1007/s10822-013-9665-3. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2013. PMID: 23877830
-
Conformational Dynamics of Ago-Mediated Silencing Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jul 1;16(7):14769-85. doi: 10.3390/ijms160714769. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26140373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geminiviral V2 Protein Suppresses Transcriptional Gene Silencing through Interaction with AGO4.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e01675-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01675-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30626668 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion and Divergence of Argonaute Genes in the Oomycete Genus Phytophthora.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 30;9:2841. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02841. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30555430 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

