Decreased apoptotic rate of alveolar macrophages of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 22792456
- PMCID: PMC3389730
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/981730
Decreased apoptotic rate of alveolar macrophages of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Introduction. Increased apoptosis of epithelial cells and decreased apoptosis of myofibroblasts are involved in the pathogenesis of IPF. The apoptotic profile of alveolar macrophages (AMs) in IPF is unclear. Aim. To investigate whether AMs of patients with IPF exhibit a different apoptotic profile compared to normal subjects. Methods. We analyzed, by immunohistochemistry, the expression of the apoptotic markers fas, fas ligand , bcl-2, and bax in AM obtained from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of 20 newly diagnosed, treatment-naive IPF patients and of 16 controls. Apoptosis of AM was evaluated by Apoptag immunohistochemistry. IPF patients received either interferon-g and corticosteroids or azathioprine and corticosteroids for six months. Results. BALF AMs undergoing apoptosis were significantly less in IPF patients. No difference was found in the expression of fas or fas ligand, bcl-2 and bax between IPF and control group. No difference was found between the respiratory function parameters of the two treatment groups after six months. A positive correlation was found between the number of bcl-2 positive stained macrophages and DLCO after treatment. Conclusions. The decreased apoptotic rate of AM of patients with IPF is not associated with decreased expression of apoptosis mediators involved in the external or internal apoptotic pathway.
Figures
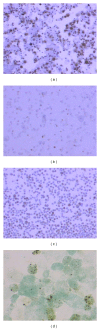
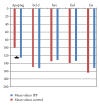
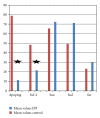
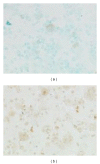
Similar articles
-
Alveolar epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis display upregulation of TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 expression with simultaneous preferential over-expression of pro-apoptotic marker p53.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jan 15;7(2):552-64. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24551275 Free PMC article.
-
The involvement of Fas-Fas ligand pathway in fibrosing lung diseases.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 Jan;20(1):53-60. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.20.1.2941. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 9870917
-
Expression of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in alveolar macrophages and lymphocytes obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in interstitial lung diseases (ILD). Assessment of IGF-I as a potential local mitogen and antiapoptotic cytokine.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2006;44(4):249-58. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2006. PMID: 17219718
-
Soluble form of fas and fas ligand in BAL fluid from patients with pulmonary fibrosis and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia.Chest. 2000 Aug;118(2):451-8. doi: 10.1378/chest.118.2.451. Chest. 2000. PMID: 10936140
-
Expression of apoptotic and antiapoptotic markers in epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Chest. 2005 Jan;127(1):266-74. doi: 10.1378/chest.127.1.266. Chest. 2005. PMID: 15653994
Cited by
-
MiR-185/AKT and miR-29a/collagen 1a pathways are activated in IPF BAL cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):74569-74581. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12740. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27769060 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of key autophagy-and mitophagy-related proteins and gene expression in BALF cells from patients with IPF and RA-ILD.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Oct;18(4):3891-3897. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9356. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30106100 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial Score and Concentrations of IL-4Rα, PAR-2, and MMP-7 in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Could Be Useful Markers for Distinguishing Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Apr 13;11(4):693. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11040693. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924683 Free PMC article.
-
SP-A2 contributes to miRNA-mediated sex differences in response to oxidative stress: pro-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-oxidant pathways are involved.Biol Sex Differ. 2017 Dec 4;8(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13293-017-0158-2. Biol Sex Differ. 2017. PMID: 29202868 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Niclosamide and Pirfenidone Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and MAPK/Nf-κB and STATs Regulated Genes.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 4;16(5):697. doi: 10.3390/ph16050697. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouros D, Antoniou KM. Current and future therapeutic approaches in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. European Respiratory Journal. 2005;26(4):693–702. - PubMed
-
- Drakopanagiotakis F, Xifteri A, Polychronopoulos V, Bouros D. Apoptosis in lung injury and fibrosis. European Respiratory Journal. 2008;32(6):1631–1638. - PubMed
-
- Tzouvelekis A, Karameris A, Tsiambas E, et al. Telomerase in pulmonary fibrosis: a link to alveolar cell apoptosis and differentiation. Pneumon. 2010;23(3):224–239.
-
- Vandivier RW, Henson PM, Douglas IS. Burying the dead: the impact of failed apoptotic cell removal (efferocytosis) on chronic inflammatory lung disease. Chest. 2006;129(6):1673–1682. - PubMed
-
- Brantly M, Avila NA, Shotelersuk V, Lucero C, Huizing M, Gahl WA. Pulmonary function and high-resolution CT findings in patients with an inherited form of pulmonary fibrosis, Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, due to mutations in HPS-1. Chest. 2000;117(1):129–136. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

