Detection of Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin production by whole-cell MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
- PMID: 22792394
- PMCID: PMC3391297
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040660
Detection of Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin production by whole-cell MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
Abstract
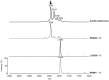
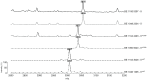
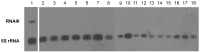
The aim of the present study was to detect the Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin using Whole-Cell (WC) Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time-of-Flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry (MS), correlate delta-toxin expression with accessory gene regulator (agr) status, and assess the prevalence of agr deficiency in clinical isolates with and without resistance to methicillin and glycopeptides. The position of the delta-toxin peak in the mass spectrum was identified using purified delta-toxin and isogenic wild type and mutant strains for agr-rnaIII, which encodes delta-toxin. Correlation between delta-toxin production and agr RNAIII expression was assessed by northern blotting. A series of 168 consecutive clinical isolates and 23 unrelated glycopeptide-intermediate S. aureus strains (GISA/heterogeneous GISA) were then tested by WC-MALDI-TOF MS. The delta-toxin peak was detected at 3005±5 Thomson, as expected for the naturally formylated delta toxin, or at 3035±5 Thomson for its G10S variant. Multivariate analysis showed that chronicity of S. aureus infection and glycopeptide resistance were significantly associated with delta-toxin deficiency (p = 0.048; CI 95%: 1.01-10.24; p = 0.023; CI 95%: 1.20-12.76, respectively). In conclusion, the S. aureus delta-toxin was identified in the WC-MALDI-TOF MS spectrum generated during routine identification procedures. Consequently, agr status can potentially predict infectious complications and rationalise application of novel virulence factor-based therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delta-toxin production deficiency in Staphylococcus aureus: a diagnostic marker of bone and joint infection chronicity linked with osteoblast invasion and biofilm formation.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015 Jun;21(6):568.e1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.01.026. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015. PMID: 25677632
-
Staphylococcus aureus interaction with phospholipid vesicles--a new method to accurately determine accessory gene regulator (agr) activity.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 30;9(1):e87270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087270. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498061 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of agr-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harbouring the class A mec complex by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Nov;304(8):1018-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25116838
-
An insight into pleiotropic regulators Agr and Sar: molecular probes paving the new way for antivirulent therapy.Future Microbiol. 2013 Oct;8(10):1339-53. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.92. Future Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24059923 Review.
-
Quorum sensing-mediated regulation of staphylococcal virulence and antibiotic resistance.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(5):669-81. doi: 10.2217/fmb.14.31. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24957093 Review.
Cited by
-
Intact Staphylococcus Enterotoxin SEB from Culture Supernatant Detected by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Feb 9;11(2):101. doi: 10.3390/toxins11020101. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30744109 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances and Ongoing Challenges in the Diagnosis of Microbial Infections by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 29;9:1097. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01097. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29896172 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Discrimination of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by MALDI-TOF MS.Pathogens. 2019 Nov 1;8(4):214. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040214. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31683799 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Local Delivery of Diflunisal Limits Bone Destruction but Fails To Improve Systemic Vancomycin Efficacy during Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Jun 23;64(7):e00182-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00182-20. Print 2020 Jun 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32340992 Free PMC article.
-
Accessory gene regulator (Agr) functionality in Staphylococcus aureus derived from lower respiratory tract infections.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 14;12(4):e0175552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175552. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28410390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bode LG, Wertheim HF, Kluytmans JA, Bogaers-Hofman D, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, et al. Sustained low prevalence of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus upon admission to hospital in The Netherlands. J Hosp Infect. 2011;79:198–201. - PubMed
-
- Novick RP, Geisinger E. Quorum sensing in staphylococci. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:541–564. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

