Fibroblast-secreted hepatocyte growth factor mediates epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in triple-negative breast cancers through paracrine activation of Met
- PMID: 22788954
- PMCID: PMC3680928
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3224
Fibroblast-secreted hepatocyte growth factor mediates epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in triple-negative breast cancers through paracrine activation of Met
Abstract
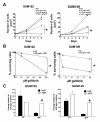
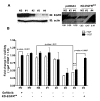
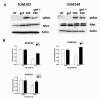
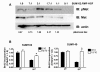
Introduction: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have shown clinical efficacy in lung, colon, and pancreatic cancers. In lung cancer, resistance to EGFR TKIs correlates with amplification of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) receptor tyrosine kinase Met. Breast cancers do not respond to EGFR TKIs, even though EGFR is overexpressed. This intrinsic resistance to EGFR TKIs in breast cancer does not correlate with Met amplification. In several tissue monoculture models of human breast cancer, Met, although expressed, is not phosphorylated, suggesting a requirement for a paracrine-produced ligand. In fact, HGF, the ligand for Met, is not expressed in epithelial cells but is secreted by fibroblasts in the tumor stroma. We have identified a number of breast cancer cell lines that are sensitive to EGFR TKIs. This sensitivity is in conflict with the observed clinical resistance to EGFR TKIs in breast cancers. Here we demonstrate that fibroblast secretion of HGF activates Met and leads to EGFR/Met crosstalk and resistance to EGFR TKIs in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Methods: The SUM102 and SUM149 TNBC cell lines were used in this study. Recombinant HGF as well as conditioned media from fibroblasts expressing HGF were used as sources for Met activation. Furthermore, we co-cultured HGF-secreting fibroblasts with Met-expressing cancer cells to mimic the paracrine HGF/Met pathway, which is active in the tumor microenvironment. Cell growth, survival, and transformation were measured by cell counting, clonogenic and MTS assays, and soft agar colony formation, respectively. Student's t test was used for all statistical analysis.
Results: Here we demonstrate that treatment of breast cancer cells sensitive to EGFR TKIs with recombinant HGF confers a resistance to EGFR TKIs. Interestingly, knocking down EGFR abrogated HGF-mediated cell survival, suggesting a crosstalk between EGFR and Met. HGF is secreted as a single-chain pro-form, which has to be proteolytically cleaved in order to activate Met. To determine whether the proteases required to activate pro-HGF were present in the breast cancer cells, we utilized a fibroblast cell line expressing pro-HGF (RMF-HGF). Addition of pro-HGF-secreting conditioned fibroblast media to TNBC cells as well as co-culturing of TNBC cells with RMF-HGF fibroblasts resulted in robust phosphorylation of Met and stimulated proliferation in the presence of an EGFR TKI.
Conclusions: Taken together, these data suggest a role for Met in clinical resistance to EGFR TKIs in breast cancer through EGFR/Met crosstalk mediated by tumor-stromal interactions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crosstalk to stromal fibroblasts induces resistance of lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Nov 1;15(21):6630-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1001. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19843665
-
Met and c-Src cooperate to compensate for loss of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase activity in breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2008 May 1;68(9):3314-22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0132. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18451158 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine receptor activation by microenvironment triggers bypass survival signals and ALK inhibitor resistance in EML4-ALK lung cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 1;18(13):3592-602. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2972. Epub 2012 May 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22553343
-
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway.Clin Lung Cancer. 2009 Jul;10(4):281-9. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.039. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19632948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor/MET in cancer progression and biomarker discovery.Cancer Sci. 2017 Mar;108(3):296-307. doi: 10.1111/cas.13156. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28064454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A tumor microenvironment-related risk model for predicting the prognosis and tumor immunity of breast cancer patients.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 18;13:927565. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.927565. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36059555 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting matriptase in breast cancer abrogates tumour progression via impairment of stromal-epithelial growth factor signalling.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 15;6:6776. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7776. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25873032 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging strategies to overcome resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Jul 15;15(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01311-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35840984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Jan 27;8(2):19. doi: 10.3390/cancers8020019. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26828520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HGF/c-MET Pathway Is a Driver and Biomarker of VEGFR-inhibitor Resistance and Vascular Remodeling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 15;23(18):5489-5501. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3216. Epub 2017 May 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28559461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baselga J, Albanell J, Ruiz A, Lluch A, Gascon P, Guillem V, Gonzalez S, Sauleda S, Marimon I, Tabernero JM, Koehler MT, Rojo F. Phase II and tumor pharmacodynamic study of gefitinib in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;14:5323–5333. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.08.326. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tan AR, Yang X, Hewitt SM, Berman A, Lepper ER, Sparreboom A, Parr AL, Figg WD, Chow C, Steinberg SM, Bacharach SL, Whatley M, Carrasquillo JA, Brahim JS, Ettenberg SA, Lipkowitz S, Swain SM. Evaluation of biologic end points and pharmacokinetics in patients with metastatic breast cancer after treatment with erlotinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J Clin Oncol. 2004;14:3080–3090. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.189. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;14:2129–2139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040938. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;14:1497–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1099314. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

